What is molluscum contagiosum (MC)?
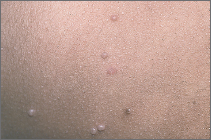
MC is a common superficial viral infection of the outer layer of skin.
MC produces something like warts; however, a different virus is involved.
Molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum
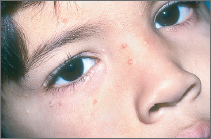
MC often appears on the face, including the eyelids. It also is seen in the armpits and on the arms and legs and sometimes on the chest and back.
In young children, MC can appear in areas of the skin that have eczema.
MC may also occur on the lower abdomen, on the inner thighs, and on the genitalia and pubic area in children and adults.
The “bumps” may be frozen lightly with liquid nitrogen applied with a cotton swab (Q-Tip) or a “freezing gun.”
A blistering agent, such as cantharidin, may be applied carefully with a toothpick to each bump every 3 to 4 weeks.
Burning and scraping (electrodesiccation and curettage) may be necessary for stubborn MC lesions.
A liquid wart medicine such as salicylic acid (Duofilm), which you can buy without a prescription, is applied carefully. It should be applied with a toothpick only to the center of the “bump.”
A little irritation usually occurs. If the area becomes too irritated, stop using the Duofilm for a day or two and then use it again when the irritation disappears.
Your health care provider may prescribe another topical or oral medication such as _______________ to try.
Outline