Clinical Classification
Cases should be classified as carcinoma of the vulva if the primary site of the growth is in the vulva. Tumors present on the vulva as secondary growths from either a genital or an extragenital site should be excluded. There should be histologic confirmation of the tumor.
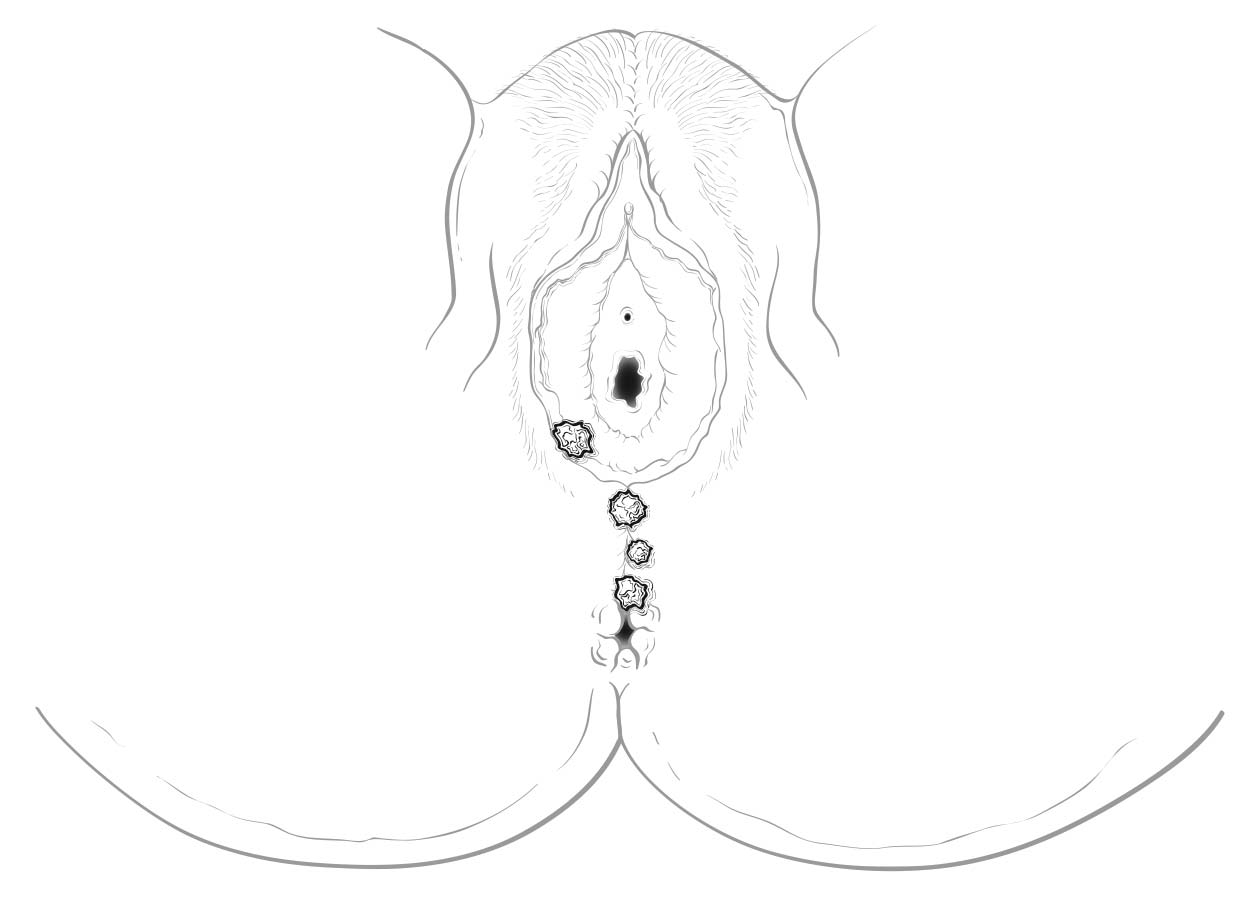
Perineal lesions represent a challenging subset of cancers that may arise from either the vulva or the perianal mucosa. Anterior perineal lesions may be considered either vulvar or perianal, and the treatment plans may be quite dissimilar. For this reason, we recommend the following: Lesions that clearly arise from the vulva and extend onto the perineum and potentially involve the anus should be classified as vulvar. Similarly, lesions that clearly arise from the anus and extend onto the perineum should be classified as perianal. For lesions localized to the perineum that do not clearly arise from either the vulva or the anus, we recommend that the clinician denote their exact location as well as his or her favored impression regarding classification. We recommend the following terminology: “perineum favor vulva” and “perineum favor anus.” We also recommend consultation with colleagues in gynecologic oncology and colorectal, general, or surgical oncology, as classification has a significant impact on treatment.
Rarely, lymph nodes are assessed by radiologic-guided fine-needle aspiration or by using imaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance (MR) imaging, or positron emission tomography (PET).
Single tumor cells or small clusters of cells not more than 0.2 mm in greatest diameter are classified as isolated tumor cells. These cells may be detected by routine histology or by immunohistochemical methods. They are designated N0(i+).
Imaging
MR imaging, CT, and PET/CT have been used in the staging of vulvar cancer. MR imaging, with its high soft tissue resolution, can stage the disease locally. CT and PET/CT may be used to assess for lymph node metastases and distant disease. Some reports suggest that PET/CT has greater sensitivity in assessing lymph node metastases in vulvar cancer. 1
TNM Components of Tumor Staging
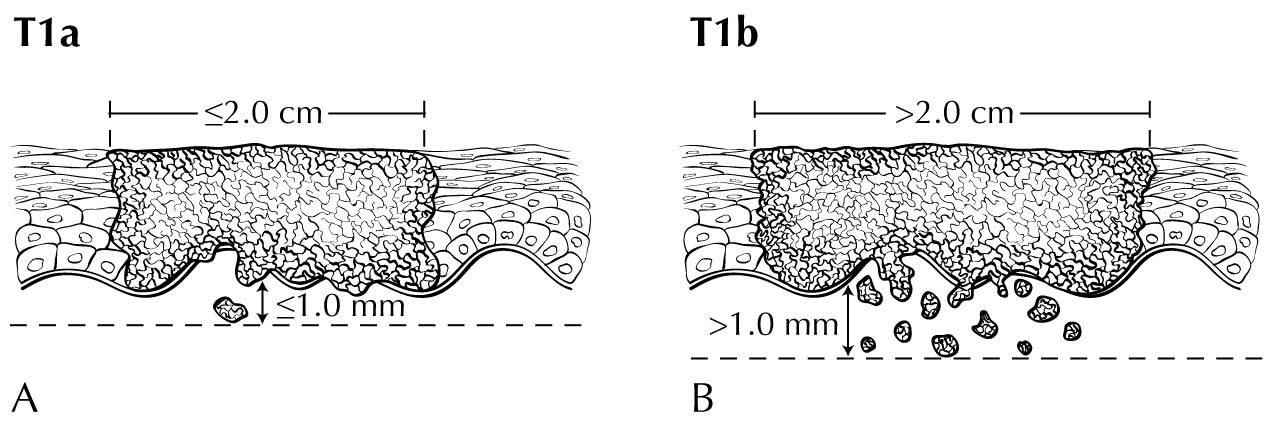
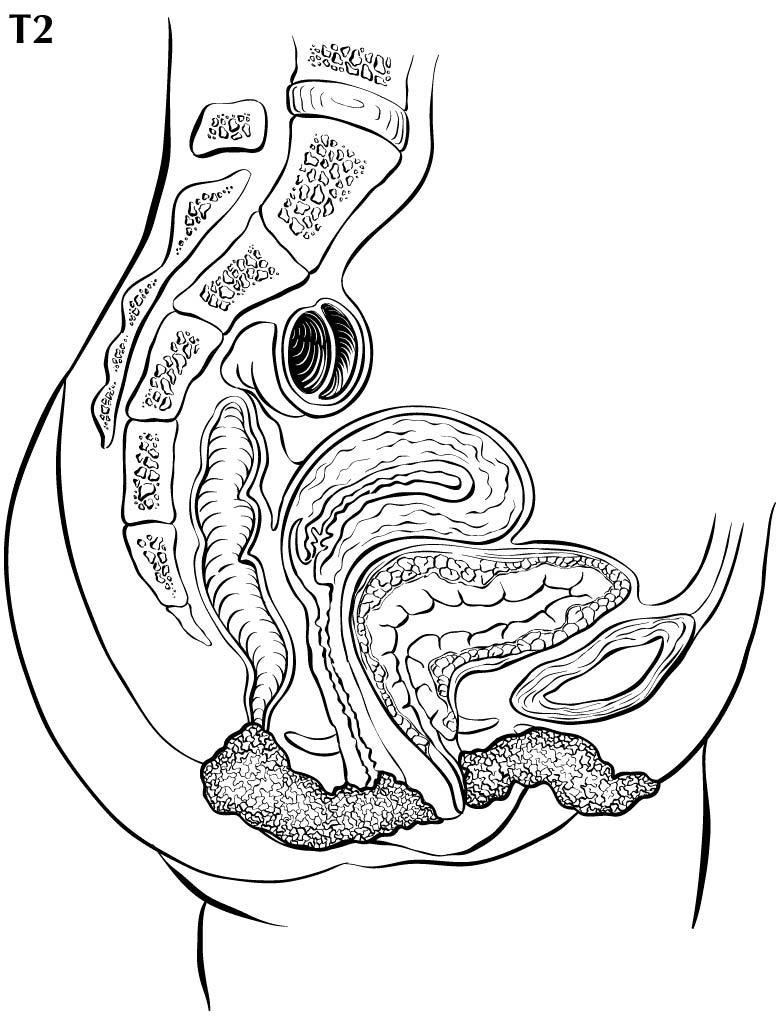
In stage T1 disease, multifocal lesions may be present. Currently, MR imaging is not used to assess the depth of invasion of the tumor into the dermal papilla. Assessing for depth of invasion of 1 mm is beyond the resolution of any currently available imaging modality. However, MR imaging may be used to measure a tumor's size, given its soft tissue resolution. If the tumor is 2 cm or smaller, it is category T1a. The disease may be visualized easier if vaginal gel is instilled and axial dynamic T1-weighted images are obtained. If the tumor is larger than 2 cm, it is category T1b. In category T2 disease, the tumor extends to the lower third of the vagina/urethra and the anus; it may be seen best on MR T2-weighted and dynamic sagittal T1-weighted sequences. In category T3 disease, the tumor may be any size and extends to the upper proximal two thirds of the urethra, the upper proximal two thirds of the vagina, the bladder mucosa, or the rectal mucosa, or it is fixed to pelvic bone. Skeletal involvement is seen best on MR non-fat-saturated T1-weighted sequences. However, involvement of other organs may be seen on MR sagittal T2-weighted and dynamic sagittal T1-weighted sequences.
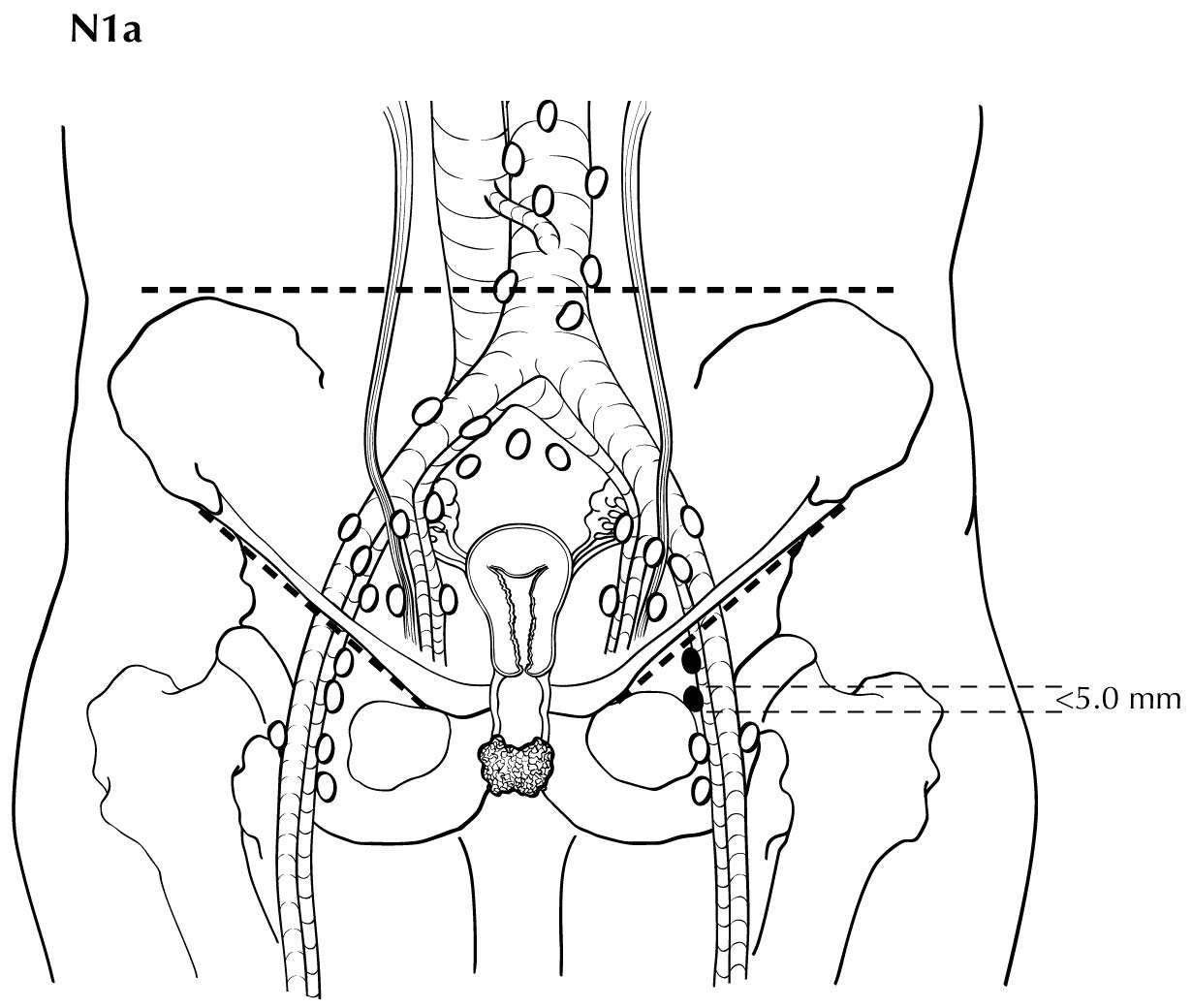
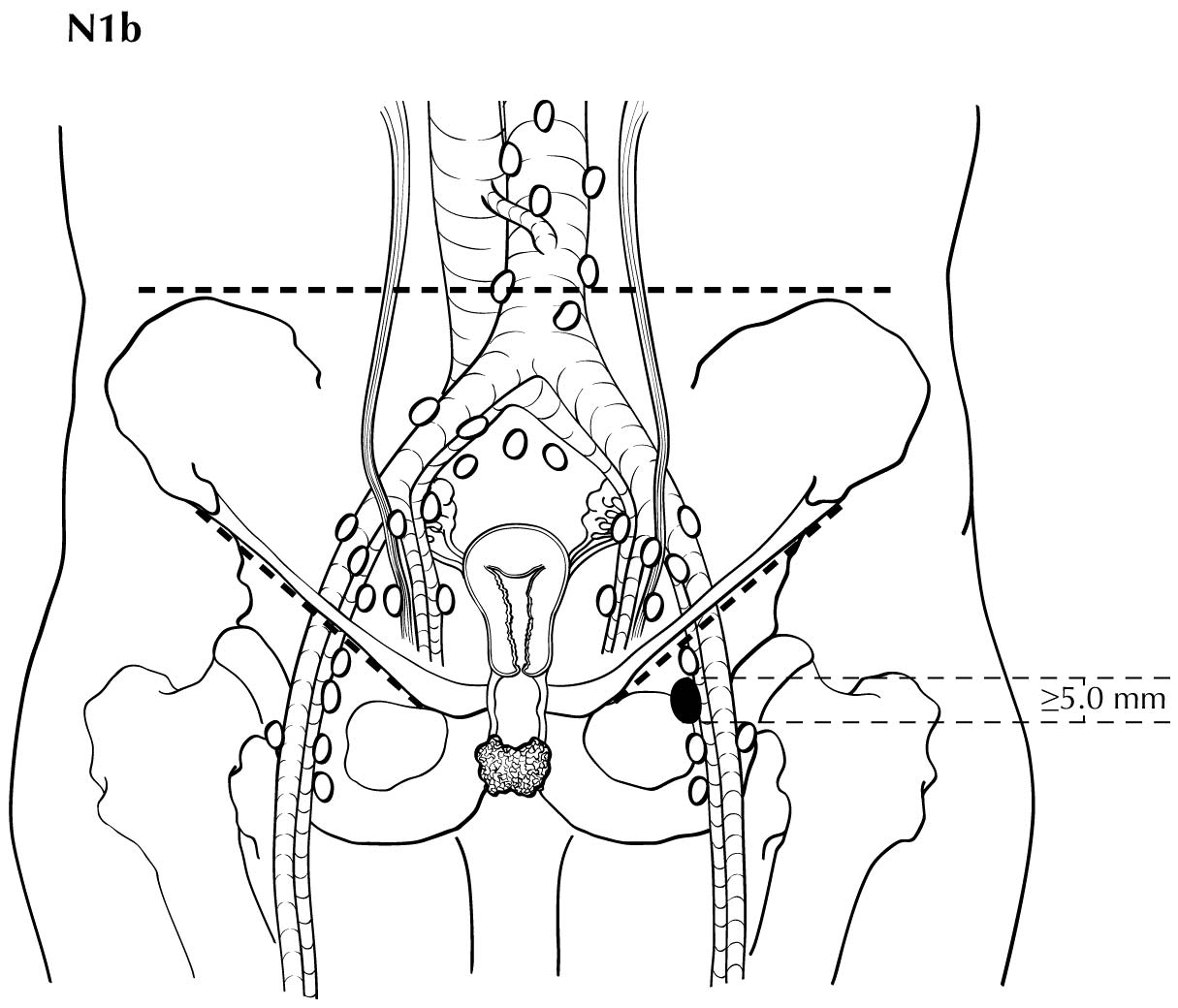
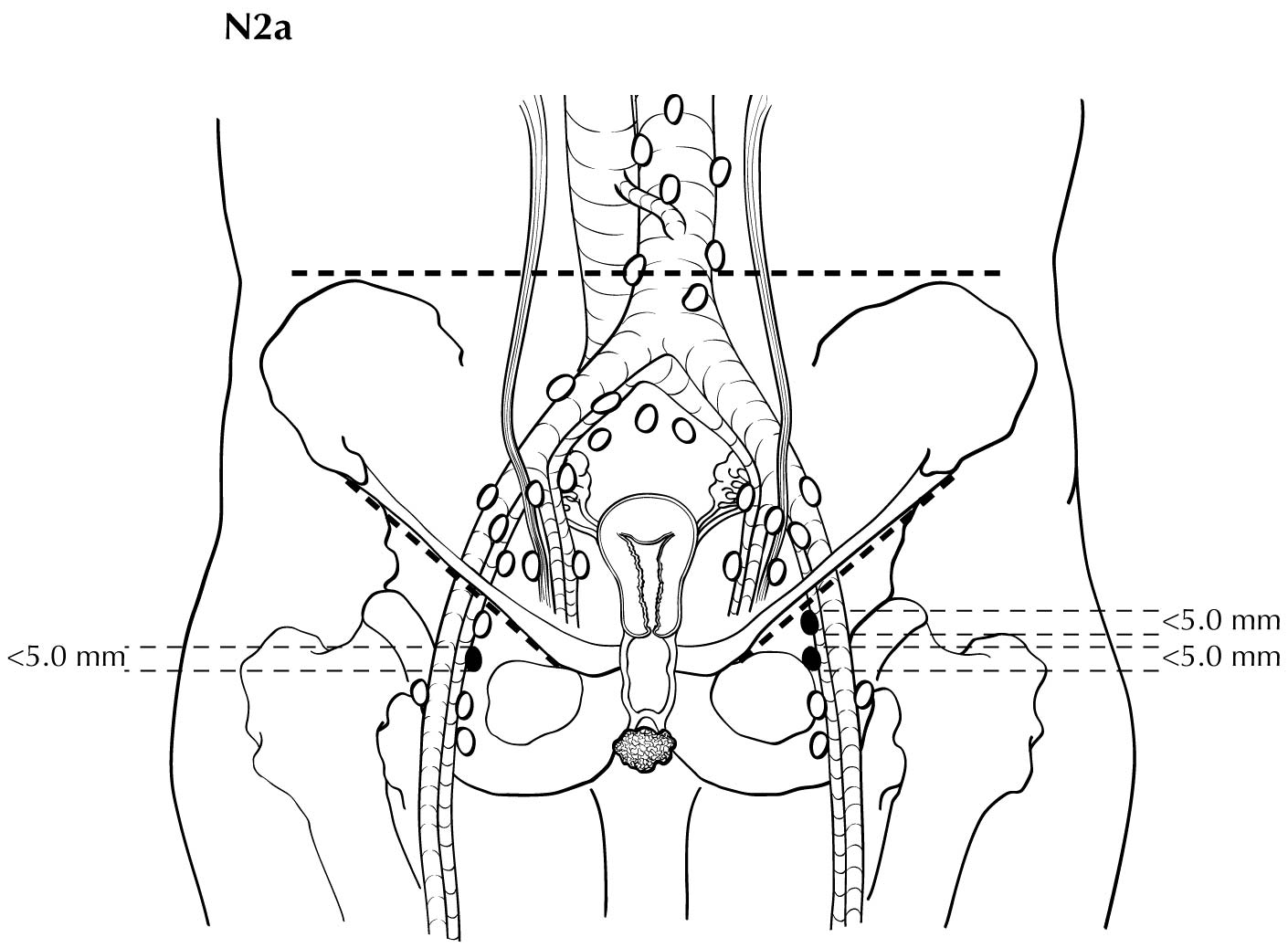
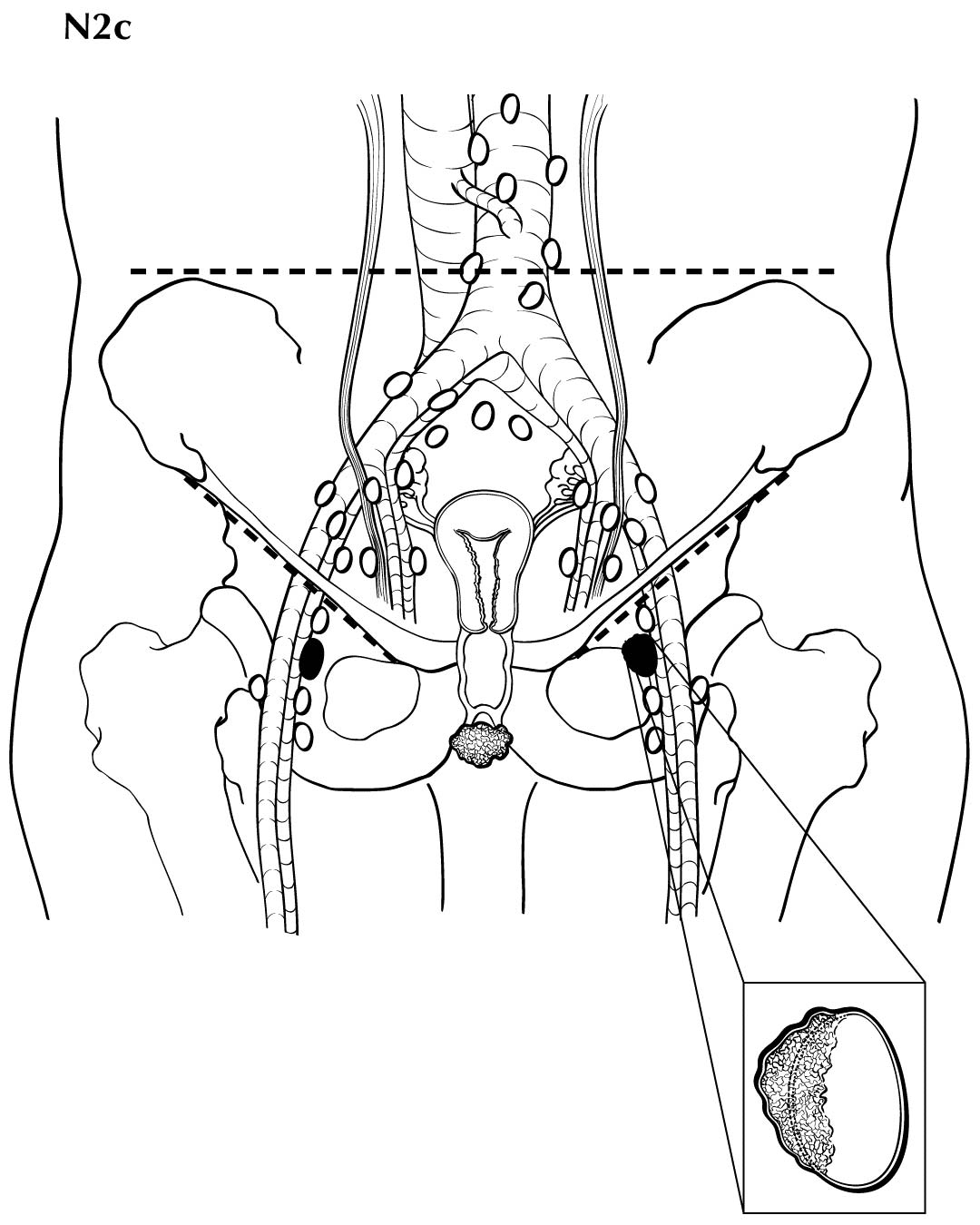
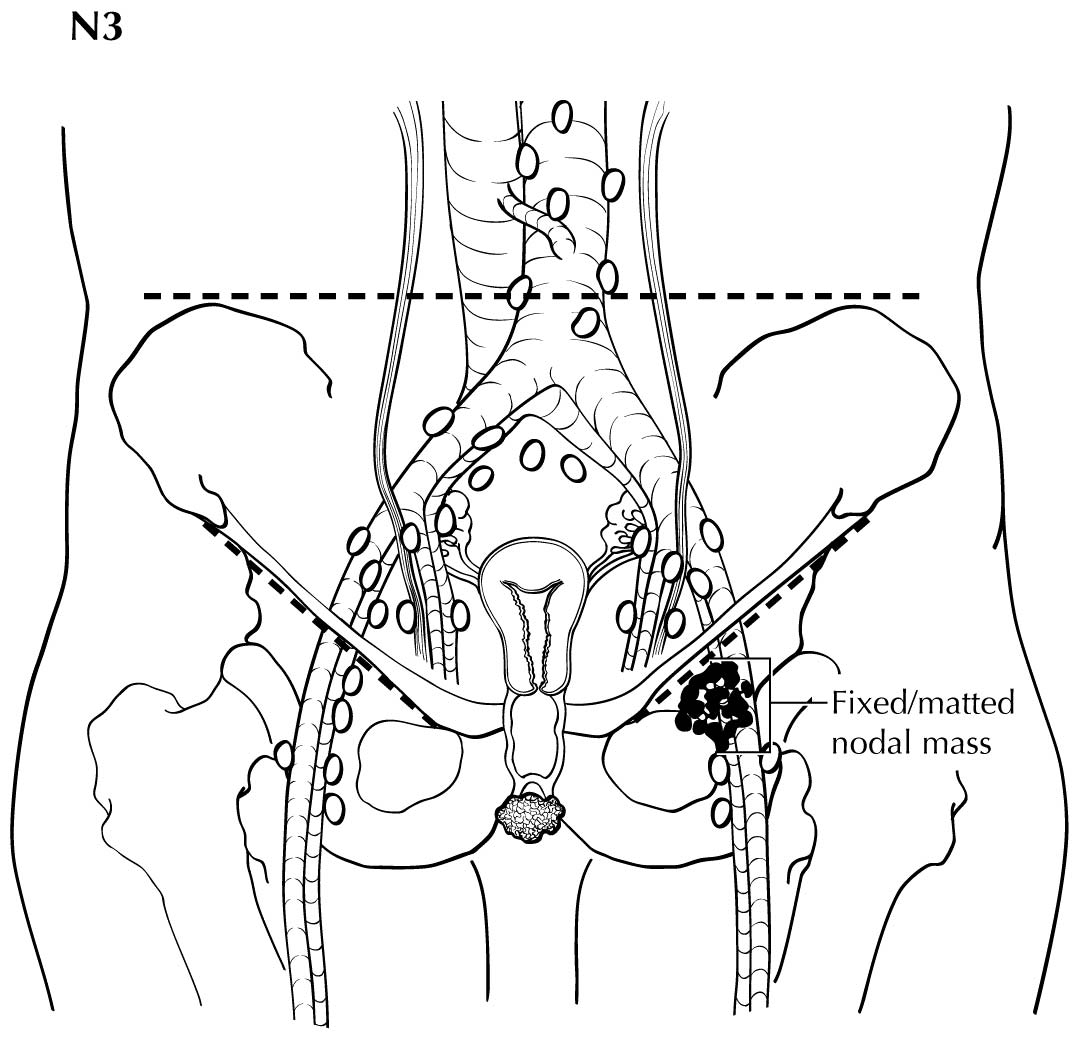
Regional nodal metastases less than 5 mm (histologically) are considered N1 disease and cannot be assessed by cross-sectional imaging. Metastatic disease less than 5 mm is beyond the scope of any in vivo imaging modality. However, some N2 disease can be identified easily based on the number and size of nodes involved. The imaging criteria used to assess lymph node metastases is based on lymph node size, with abnormal being greater than 1 cm in the short axial dimension. However, because there may be false positive causes of enlarged nodes from benign disease, PET/CT is considered superior in assessing lymph node metastases. Metabolically active lymph nodes of any size on PET/CT are considered metastatic. Ulceration and immobility of the lymph nodes may be assessed better on physical examination.
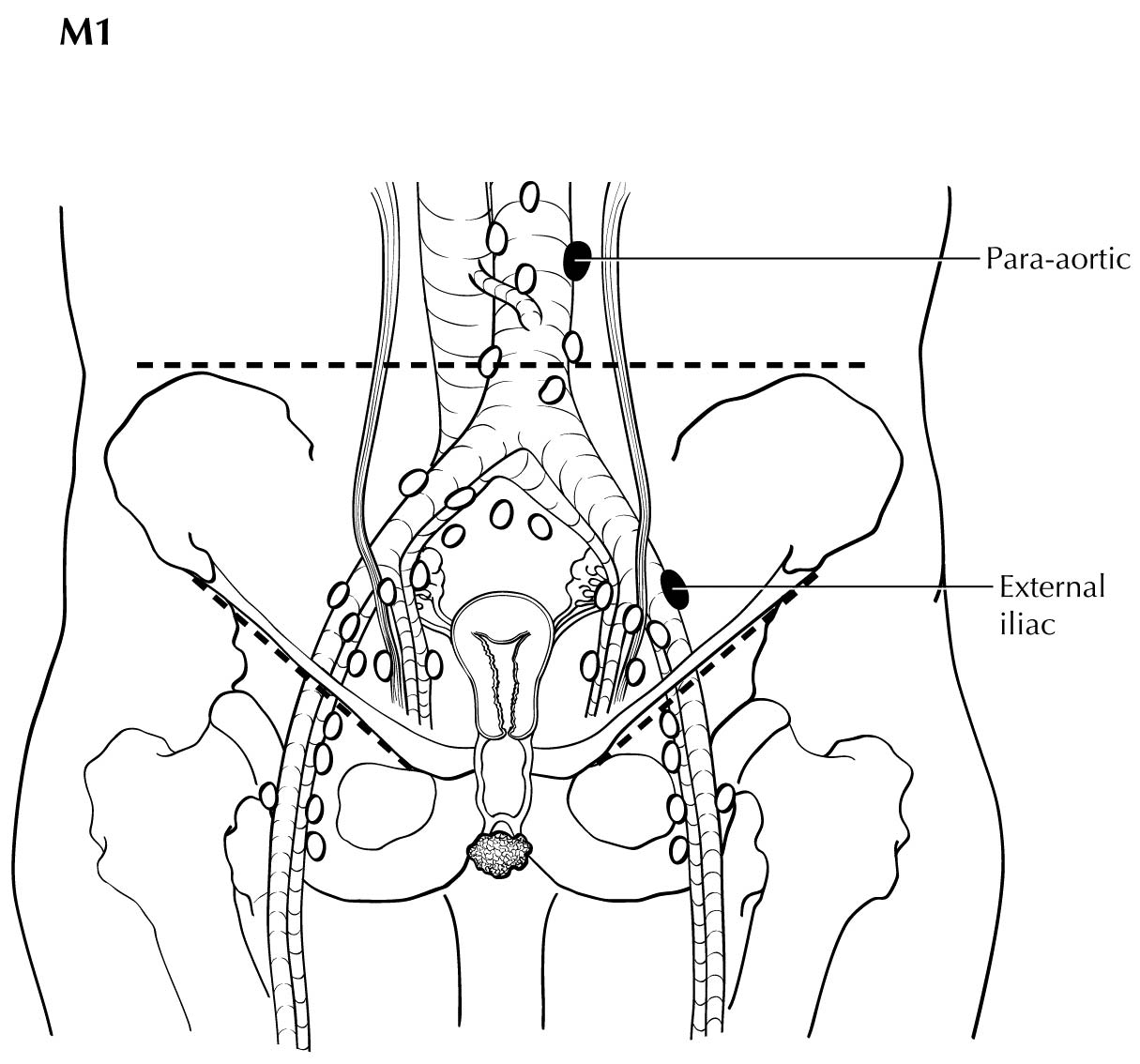
The presence of pelvic lymph node metastases or lung, visceral, or bone metastases is considered M1 disease, and PET/CT is superior in assessing its extent. If PET/CT is not available, contrast-enhanced CT may be used.
Suggested Imaging Report Format
- Primary tumor
- Size less than or equal to 2 cm or greater than 2 cm
- Local extent
- Involvement of the bladder and the rectum, vagina, and urethra
- Description of the site, number, and laterality of inguinal lymph nodes
- Pelvic and distant lymph node involvement and extrapelvic disease
Pathological Classification
FIGO uses surgical/pathological staging for vulvar cancer. Stage should be assigned at the time of definitive surgical treatment before radiation or chemotherapy. If chemotherapy, radiation, or a combination of both treatment modalities is the initial mode of therapy, clinical staging should be used. The stage cannot be changed on the basis of disease progression or recurrence or on the basis of response to initial radiation or chemotherapy that precedes primary tumor resection.
For pN, histologic examination of regional lymphadenectomy specimens ordinarily includes six or more lymph nodes. For TNM staging, cases with fewer than six resected nodes should be classified using the TNM pathological classification based on the status of those nodes (e.g., pN0, pN1) according to the general rules of TNM. The number of resected and positive nodes should be recorded (note that FIGO classifies cases with less than six nodes resected as pNX). The concept of sentinel lymph node mapping, in which only one or two key nodes are removed, currently is being investigated. In most cases, regional lymph nodes are assessed surgically (via inguinal-femoral lymphadenectomy). Included in the 8 th Edition is the opportunity to denote a micrometastatic lymph node using the N1mi or N2mi category. The current revisions to staging adopted reflect the recognition that the number and size of lymph node metastases more accurately reflect prognosis.