A.11. What are the common indications for VV-ECMO?
Answer:
In VV-ECMO, an oxygenator is placed in series between a drainage cannula (usually internal jugular vein) and a venous return cannula (usually femoral vein) (Figure 6.3). However, using a dual-lumen cannula (Figure 6.4) eliminates the need for separate cannulas. Since the blood is returned to the venous circulation, CO is not augmented. After deoxygenated venous blood passes through the pump and oxygenator, it returns to the venous circulation, where it mixes with systemic venous blood and passes via the pulmonary circulation to the left side of the heart and to the systemic circulation. As such, there is no cardiac support provided by VV-ECMO. VV-ECMO is primarily used for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) (eg, due to COVID-19), as a bridge to lung transplantation, and as support for surgical lung or airway procedures.
Figure 6.3.: Cannula Configuration for Dual-Cannula Veno-Venous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (VV-ECMO).
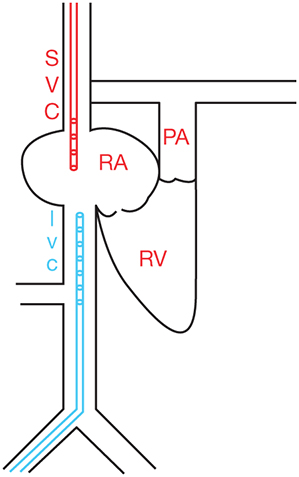
Cannula configuration for dual-cannula veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VV-ECMO). Drainage cannula is placed in the IVC and return cannula is placed in the SVC. Deoxygenated blood (blue) is drained from the femoral cannula and oxygenated blood (red) is returned to the internal jugular vein. IVC, inferior vena cava; PA, pulmonary artery; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle; SVC, superior vena cava; V-V, veno-venous.
Figure 6.4.: Cannula Configuration of Single-Cannula (Dual-Lumen) Veno-Venous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (VV-ECMO).
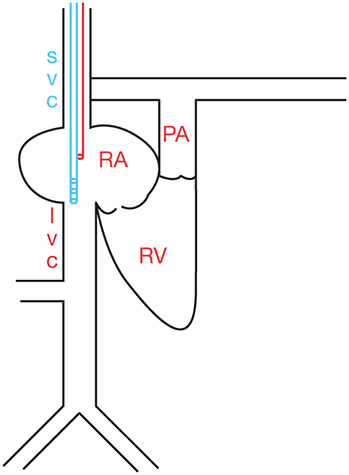
Cannula configuration of single-cannula (dual-lumen) veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VV-ECMO). Drainage lumen is positioned in the IVC while return lumen is positioned toward right atrium. Deoxygenated blood (blue) is drained from the distal lumen and oxygenated blood (red) is returned through the proximal lumen near the right atrium. IVC, inferior vena cava; PA, pulmonary artery; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle; SVC, superior vena cava; V-V, veno-venous.
References
- ELSO Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Extracorporeal Life Support Extracorporeal Life Support Organization, Version 1.4. Accessed May 14, 2023. www.elso.org
- Combes A, Hajage D, Capellier G, et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1965-1975.


