- Blue top tube
- 3-5 mL of venous blood
Additional information
- The ratio of anticoagulant (sodium citrate) to blood (1:9) is critical
- Handle sample gently to prevent hemolysis
- Place the sample on ice and send it to lab promptly
- Blue topped vacuum tubes keep the prothrombin levels stable at room temperature for 12 hrs if left capped.
- Prothrombin time (PT) is a test that measures the "extrinsic system" of clotting factors. These include factors I (fibrinogen), II (prothrombin), V, VII, and X. If any of these factors are deficient, the PT is prolonged.
- This test measures the time required for a firm fibrin clot to form after addition of tissue thromboplastin (factor III) and calcium to the blood sample
- Prothrombin is a vitamin K dependent protein primarily synthesized in the liver that is involved in blood coagulation
- In clinical practice; the most common use of this test is to monitor patients on warfarin (Coumadin®) therapy.
- The International Normalized Ratio (INR) is a method of standardizing prothrombin time results. It has been devised to compare prothrombin time results among labs using different test methods
- The INR value is calculated by the formula:
INR = (PT patient/PT normal)ISI
Where:
- PT patient = Patient's prothrombin time
- PT normal = Mean normal PT for the laboratory system
- ISI = International Sensitivity Index assigned to the system
- The clinical utility of the PT test includes:
- Evaluation of the clotting ability of the following plasma coagulation factors (extrinsic pathway of the coagulation sequence):
- Factor I (Fibrinogen)
- Factor II (Prothrombin)
- Factor V
- Factor VII
- Factor X
- Evaluation of the response to anticoagulant therapy [Usually to warfarin (Coumadin®)], to achieve therapeutic efficacy
- Screening of individuals who are prone to bleeding, prior to surgical, obstetric, dental, or invasive diagnostic procedures
- Evaluation of the causes of bruising and abnormal bleeding such as
- Epistaxis
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
- Gingival bleeding
- Hematomas
- Hematuria
- Menorrhagia
- Any other abnormal bleeding
- Evaluation of:
- Liver disease
- Protein deficiency
- Fat malabsorption
- Disfibrinogenemia
- Screening for prothrombin deficiency
- Screening for vitamin K deficiency
- INR values allows more consistent monitoring of anticoagulant therapy with warfarin (Coumadin®)
- PT performed along with APTT is of more significance:
- Prolonged PT with normal APTT can occur only with factor VII deficiency
- Normal PT with prolonged APTT could indicate a deficiency in factors XII, XI, IX, and VIII as well as VIII: C (von Willebrand factor)
Additional information
- Coagulation disorders where the PT is not affected include the following:
- Christmas disease (factor IX deficiency)
- Hemophilia A (factor VIII deficiency)
- Platelet disorders (idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura)
- Polycythemia vera
- Tannin disease
- von Willebrand's disease
- Related laboratory tests include:
- Alanine aminotransferase
- Aspartate aminotransferase
- Bilirubin
- Bleeding time
- Coagulation factors
- Complete blood count
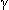 -glutamyltranspeptidase
-glutamyltranspeptidase- Partial thromboplastin time
- Platelet count
- Prothrombin consumption time
- Vitamin K
zConsult your laboratory for their normal ranges as these may vary somewhat from the ones listed below.
| INR | Seconds | |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | 0.9-1.2 | 11.0-13.0 |
| Critical values | >6.0 | Varies by reagent |
Therapeutic levels by condition
| INR | |
|---|---|
| Atrial fibrillation | 2.0-3.0 |
| Deep venous thrombosis | 2.0-3.0 |
| Mechanical heart valves | 2.0-3.5* |
| Pulmonary embolism | 2.0-3.5** |
| Systemic embolism (Recurrent) | 2.5-3.5 |
| Valvular heart disease | 2.0-3.0 |
* Varies with valve type and position
** Some sources recommend 2.5-3.5 whereas others recommend 2.0-3.0 for pulmonary embolus
Conditions associated with prolonged PT levels include:
- Deficiency of coagulation factors
- Factor I (Fibrinogen)
- Factor II (Prothrombin)
- Factor V (Proaccelerin)
- Factor VII (Proconvertin)
- Factor X (Stuart Factor)
- Vitamin K deficiency
- Newborns of mothers with vitamin K deficiency
- Hemorrhagic disease of the newborn
- Premature newborns
- Liver disease:
- Alcoholic hepatitis
- Cirrhosis
- Biliary obstruction
- Current anticoagulant therapy with warfarin (Coumadin®)
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
- Hypofibrinogenemia and dysfibrinogenemias
- Poor fat absorption as in
- Celiac disease
- Chronic diarrhea
- Sprue
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Massive blood transfusion
Drugs and substances associated with an increase in PT include:
- Acetaminophen
- Acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin)
- Alcohol in excess
- Allopurinol
- Amiodarone
- Anabolic steroids
- Anisindione
- Anistreplase
- Antipyrine
- Carbenicillin
- Cephalosporins
- Chlorthalidone
- Cholestyramine resin
- Cimetidine
- Clofibrate
- Corticotropin
- Demeclocycline
- Dextrothyroxine
- Diazoxide
- Diflunisal
- Diphenylhydantoin
- Diuretics
- Doxycycline
- Erythromycin
- Glucagon
- Heparin IV (within 5 hrs of sample collection)
- Hydroxyzine
- Indomethacin
- Isoniazid
- Laxatives
- Mefenamic acid
- Mercaptopurine
- Methimazole
- Metronidazole
- Miconazole
- Nalidixic acid
- Neomycin
- Niacin
- Oral hypoglycemics
- Oxyphenbutazone
- Para-aminosalicylic acid
- Phenothiazides
- Phenylbutazone
- Phenytoin
- Propylthiouracil
- Quinidine
- Quinine
- Sulfachlorpyridazine
- Thyroid hormones
- Vitamin A
- Warfarin
Falsely prolonged PT may be seen in the following:
- Alcoholism or excessive alcohol ingestion
- Plasma fibrinogen levels >100 mg/dl
- Salicylates >1 g/day
- Failure to fill the collection tube completely
- Inadequate mixing of the sample and the anticoagulant
- Delay in sending the sample to the lab
Conditions associated with reduced PT levels include:
- Ovarian hyperfunction
- Regional enteritis or ileitis
- Thrombophlebitis
Drugs and substances associated with reduced PT levels include:
- Amobarbital
- Antacids
- Antihistamines
- Barbiturates
- Caffeine
- Carbamazepine
- Cardiac glycosides
- Chloral hydrate
- Chlordane
- Colchicines
- Corticosteroids
- Diphenhydramine
- Diuretics
- Glutethimide
- Griseofulvin
- Oral contraceptives
- Penicillin
- Primidone
- Progestin-estrogen combinations
- Pyrazinamide
- Rifampin
- Simethicone
- Spironolactone
- Theophylline
- Tolbutamide
- Vitamin K
- Xanthines
Falsely reduced PT may be seen in the following conditions:
- Diarrhea and vomiting
- Venipuncture technique is traumatic
- Sample collected in the tube is not filled properly
- Prolonged storage of plasma at 4°C
Patients on warfarin (Coumadin®) therapy can antagonize warfarin (thus decreasing their PT/INR) by having dietary consumption of foods high in vitamin K such as:
- Broccoli
- Cauliflower
- Collards
- Chickpeas
- Green tea
- Kale
- Liver
- Parsley
- Pork liver
- Soybean products
- Spinach
- Swiss chart
- Turnip greens
- Berkovsky A et al. A modified method of prothrombin time/International Normalised Ratio determination in capillary blood and monitoring oral anticoagulant therapy. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2006;44(10):1214-7.
- Caldwell SH et al. Coagulation disorders and hemostasis in liver disease: pathophysiology and critical assessment of current management. Hepatology. 2006 Oct;44(4):1039-46.
- Couris A et al. Dietary vitamin K variability affects International Normalized Ratio (INR) coagulation indices. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2006 Mar;76(2):65-74.
- Hutten BA et al. Incidence of recurrent thromboembolic and bleeding complications among patients with venous thromboembolism in relation to both malignancy and achieved international normalized ratio: a retrospective analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2000 Sep;18(17):3078-83.
- Koertke et al. INR self-management permits lower anticoagulation levels after mechanical heart valve replacement. Circulation. 2003 Sep 9;108 Suppl 1:II75-8.
- LabTestsOnline®. PT and INR. [Homepage on the Internet] ©2001-2006. Last reviewed on May 6, 2005. Last accessed on November 7, 2006. Available at URL: http://www.labtestsonline.org/understanding/analytes/pt/sample.html
- Meijer P et al. A National Field Study of Quality Assessment of CoaguChek Point-of-Care Testing Prothrombin Time Monitors. Am I Clin Pathol. 2006 Nov;126(5):756-61.
- Stein, PD et al. Antithrombotic therapy in patients with mechanical and biological prosthetic heart valves. Chest 1998;114;602-610.