(See Figure 11.35.1.)
Critical
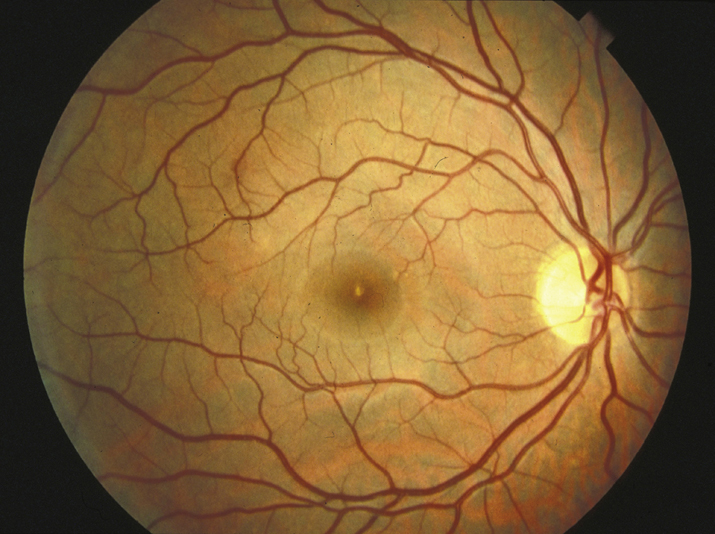
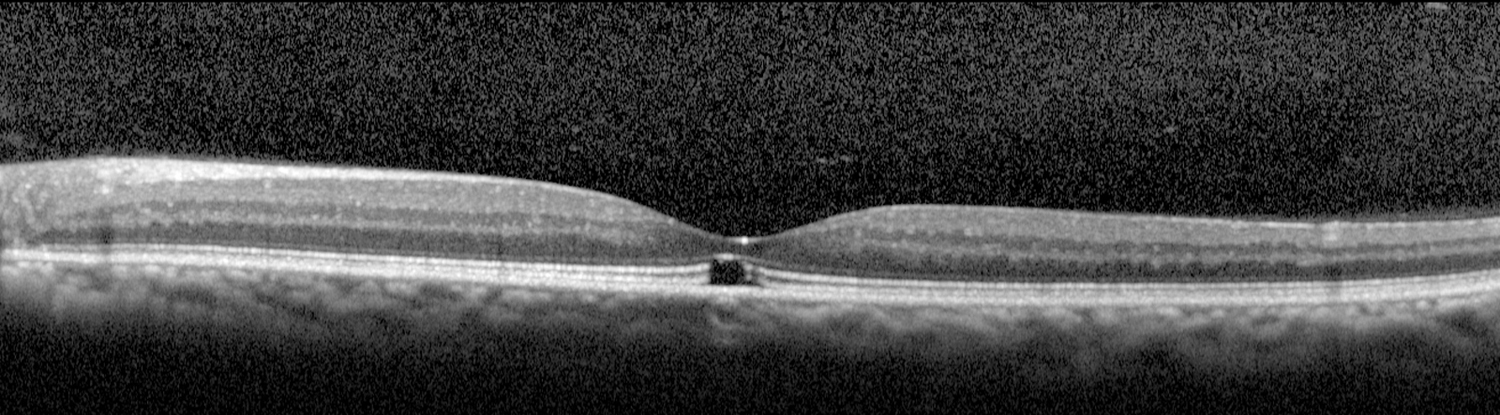
Acute findings include a yellow-white spot in the fovea with or without surrounding granular gray pigmentation. Classic late finding is a red, sharply demarcated lesion in the fovea.
Other
Visual acuity usually ranges from 20/25 to 20/100. Amsler grid testing may reveal central or paracentral scotoma. Resolution of acute findings within several weeks may leave a variable appearance to the fovea (e.g., pigmentary disturbance, lamellar hole, normal appearance, etc). Eyes with better initial visual acuities are more likely to have unremarkable fundoscopic examinations at follow up.