- Orbital cellulitis from adjacent ethmoiditis: Most common cause of proptosis in children. It is of paramount importance to quickly rule out this etiology. See 7.3.1, ORBITAL CELLULITIS.
- Dermoid and epidermoid cysts: Manifest clinically from birth to young adulthood and enlarge slowly. Preseptal dermoid cysts may become symptomatic in childhood and are most commonly found in the temporal upper eyelid or brow, and less often in the medial upper eyelid. The palpable, smooth mass may be mobile or fixed to the periosteum. Posterior dermoids typically become symptomatic in adulthood and may cause proptosis or globe displacement. Dermoid cyst rupture may mimic orbital cellulitis. The B-scan US, when used, reveals a cystic lesion with good transmission of echoes. Because of the cystic configuration and specific signal properties, CT and MRI are usually diagnostic. See 14.3, MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING.
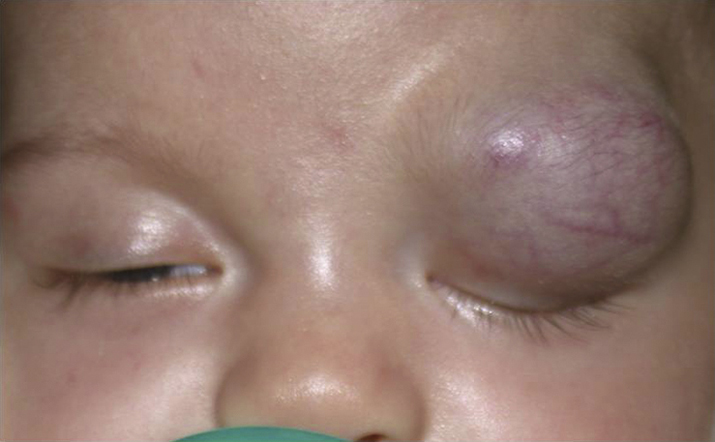
- Hemangioma of infancy (capillary hemangioma): Seen from birth to 2 years, generally show slow progressive growth over the first 6 to 9 months with slow involution thereafter. May be observed through the eyelid as a bluish mass or be accompanied by a red hemangioma of the skin (strawberry nevus, stork bite), which blanches with pressure (see Figure 7.4.1.1). Proptosis may be exacerbated by crying. It can enlarge over 6 to 12 months, but spontaneously regresses over the following several years. Not to be confused with the unrelated cavernous venous malformation (cavernous hemangioma) of the orbit, typically seen in adults.
- Rhabdomyosarcoma: Average age of presentation is 8 to 10 years, but may occur from infancy to adulthood. May present with explosive proptosis, edema of the eyelids, a palpable eyelid lesion or subconjunctival mass, new-onset ptosis or strabismus, or a history of nosebleeds. Hallmarks are rapid onset and progression. Pain may occur in a minority of cases. Urgent biopsy and referral to a pediatric oncologist is warranted if suspected.
- Metastatic neuroblastoma: Seen during the first few years of life (usually by the age of 5 years). Abrupt presentation with unilateral or bilateral proptosis, eyelid ecchymosis, and globe displacement. The child is usually systemically ill, and 80% to 90% of patients presenting with orbital involvement already have a known history of neuroblastoma. Note that metastatic neuroblastoma may also present as an isolated Horner syndrome in a child due to metastasis to the lung apex. Prognosis decreases with age.
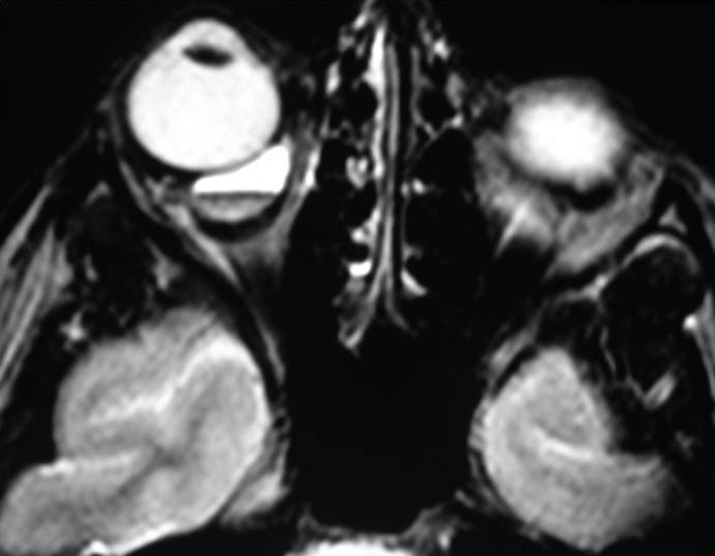
- Lymphangioma: Usually seen in the first 2 decades of life with a slowly progressive course but may abruptly worsen if the tumor spontaneously bleeds. Proptosis may be intermittent and exacerbated by upper respiratory tract infections. Lymphangioma may present as an atraumatic eyelid ecchymosis. Concomitant conjunctival, eyelid, or oropharyngeal lymphangiomas may be noted (a conjunctival lesion appears as a multicystic mass). MRI is often diagnostic. The B-scan US, when used, often reveals cystic spaces. See Figure 7.4.1.2.
- Optic nerve glioma (juvenile pilocytic astrocytoma): Usually first seen at the age of 2 to 6 years and is slowly progressive. The presentation includes painless axial proptosis with decreased visual acuity and a relative afferent pupillary defect. Optic nerve atrophy or swelling may be present. May be associated with neurofibromatosis (types I and II), in which case it may be bilateral. Prognosis decreases with chiasmal or hypothalamic involvement. See 13.13, PHAKOMATOSES.
- Plexiform neurofibroma: Seen in the first decade of life and is pathognomonic for neurofibromatosis type I. Ptosis, eyelid hypertrophy, S-shaped deformity of the upper eyelid, or pulsating proptosis (from the absence of the greater sphenoid wing) may be present. Facial asymmetry and a palpable anterior orbital mass may also be evident. See 13.13, PHAKOMATOSES.
- Leukemia (granulocytic sarcoma): Seen in the first decade of life with rapidly evolving unilateral or bilateral proptosis and, occasionally, swelling of the temporal fossa area due to a mass. Typically, granulocytic sarcoma precedes blood or bone marrow signs of leukemia (usually acute myelogenous leukemia) by several months. Any patient with a biopsy-proven granulocytic sarcoma of the orbit must be closely followed by an oncologist for leukemia development. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia can also produce unilateral or bilateral proptosis.
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH): May present in the orbit as a rapidly progressive mass with bony erosion on imaging. Three variants are encountered in the orbit: (1) multifocal, multisystem LCH (Letterer–Siwe disease) occurs in children <2 years old with an aggressive multisystem course and poor prognosis; (2) multifocal unisystem LCH (Hand–Schüller–Christian disease) occurs in children 2 to 10 years of age. The classic triad includes exophthalmos, lytic bone lesions, and diabetes insipidus from pituitary stalk infiltration; (3) unifocal LCH (eosinophilic granuloma) typically causes bony erosion in the superolateral orbit suggestive of malignancy. Occurs in older children and adults. Systemic progression occurs in only a minority of cases.