Symptoms
Pain, decreased vision, and loss of fluid from eye. History of trauma, fall, or sharp object entering globe.
Signs
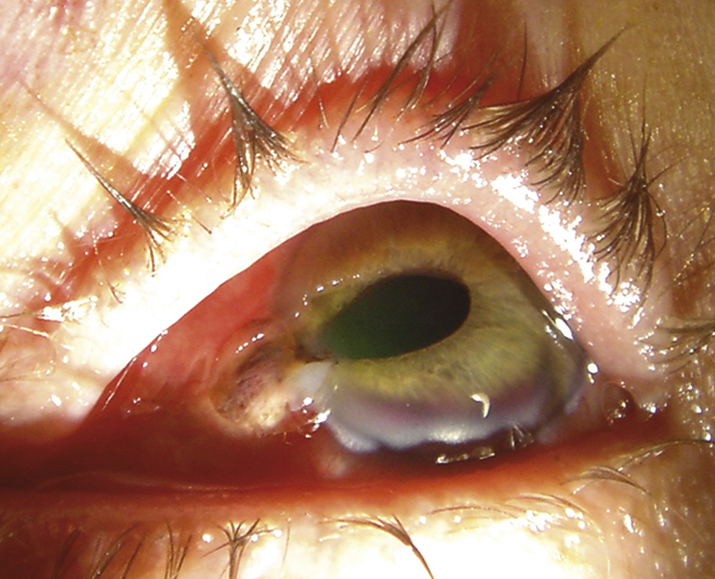
(See Figure 3.14.1.)
Critical
Full-thickness scleral or corneal laceration, severe subconjunctival hemorrhage (especially involving 360 degrees of bulbar conjunctiva, often bullous), a deep or shallow AC compared to the fellow eye, a peaked or irregular pupil, iris TIDs, lens material or vitreous in the AC, foreign body tract or new opacity in the lens, or extraocular motility limitation (greatest in the direction of rupture). Intraocular contents may be outside of the globe.
Other
Low IOP (may also be normal or rarely increased), iridodialysis, cyclodialysis, hyphema, periorbital ecchymosis, VH, and dislocated or subluxed lens. Commotio retinae, choroidal rupture, and retinal breaks may be seen but are often obscured by VH.
Workup/Treatment
Once a ruptured globe is diagnosed, further examination should be deferred until the time of surgical repair in the operating room. This is to avoid placing any pressure on the globe and risking extrusion of intraocular contents. Diagnosis should be made by penlight, indirect ophthalmoscope, or, if possible, slit lamp examination (with minimal manipulation). Once the diagnosis is made, the following measures should be taken:
- Protect the eye with a hard shield at all times. Do not patch the eye.
- CT scan of the brain and orbits (axial, coronal, and parasagittal views with 1-mm sections) to rule out IOFB.
- Gentle B-scan ultrasound may be needed to localize posterior rupture site(s) or to rule out IOFBs not visible on CT scan (nonmetallic, wood, etc.). However, B-scan should not be done in patients with an obvious anterior rupture due to the risk of extruding intraocular contents. A trained ophthalmologist should evaluate the patient before B-scan or any other manipulation is performed on a ruptured globe suspect.
- Admit the patient to the hospital with no food or drink (NPO).
- Place the patient on bed rest with bathroom privileges. Avoid strenuous activities, bending, and Valsalva maneuvers.
- Systemic antibiotics should be administered within 6 hours of injury. For adults, give cefazolin 1 g i.v. q8h or vancomycin 1 g i.v. q12h, and moxifloxacin 400 mg i.v. daily (or an equivalent fluoroquinolone). For children ≤12 years, give cefazolin 25 to 50 mg/kg/d i.v. in three divided doses and gentamicin 2 mg/kg i.v. q8h. Some groups recommend 48 hours of intravenous antibiotics perioperatively. A 1-week antibiotic course is typically completed postoperatively with a broad-spectrum fluoroquinolone (e.g., levofloxacin 750 mg p.o. daily).
- Administer tetanus toxoid p.r.n. (see APPENDIX 2, TETANUS PROPHYLAXIS).
- Administer antiemetics (e.g., ondansetron 4 or 8 mg q4–8h) p.r.n. for nausea and vomiting to prevent Valsalva and possible expulsion of intraocular contents.
- Administer pain medicine before and after surgery p.r.n. (often intravenous).
- Determine time of the patient’s last meal. Timing of surgical repair is often influenced by this information.
- Arrange for surgical repair to be done as soon as possible.
Antibiotic doses may need to be reduced if renal function is impaired. Gentamicin peak and trough levels are obtained 1/2 hour before and after the fifth dose, and blood urea nitrogen and creatinine levels are evaluated every other day. |
In any severely traumatized eye in which there is no chance of restoring vision, potential enucleation should be discussed with the patient early on. This procedure should be performed within 7 to 14 days after the trauma to minimize the rare occurrence of sympathetic ophthalmia. |
Infection is more likely to occur in eyes with dirty injuries, retained IOFBs and rupture of lens capsule and in patients with a long delay until primary surgical repair. In patients at high risk of infection, some groups recommend intravitreal antibiotics at the time of surgical closure (see 12.15, TRAUMATIC ENDOPHTHALMITIS).
Several studies have examined prognostic factors for ocular trauma and open globe injuries. One commonly used and validated system is the Ocular Trauma Score (OTS). See Tables 3.14.1 and 3.14.2. |
3-14.1 Calculating the OTS
|
LP/HM, light perception/hand motion; NLP, no light perception.
3-14.2 Visual Prognosis per OTS
|
OTS, Ocular Trauma Score.