Symptoms
Decreased vision or asymptomatic; history of recent ocular trauma.
Signs
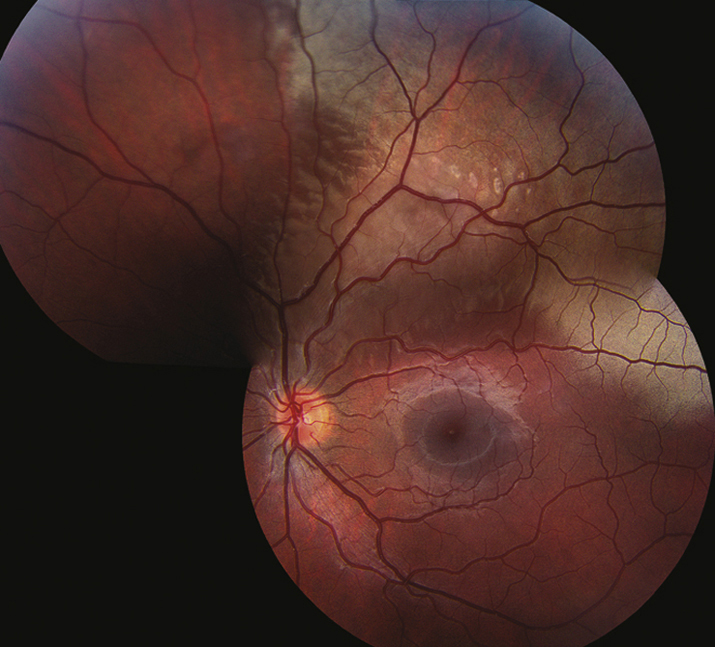
(See Figure 3.17.1.)
Critical
Confluent area of retinal whitening in the periphery or posterior pole (Berlin edema). Cherry-red spot may be present with Berlin edema. The retinal blood vessels are undisturbed in the area of retinal whitening.
Other
Additional signs of ocular trauma, such as retinal hemorrhages, may be noted.
Visual acuity does not always correlate with the degree of retinal whitening. |
Etiology
Blunt trauma to the globe causes shock waves which disrupt the photoreceptors. Retinal whitening is the result of fragmentation of the photoreceptor outer segments and intracellular edema of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). The inner retinal layers may also be involved depending on the force of injury.
Differential Diagnosis
- Retinal detachment: Retina elevated associated with retinal break or dialysis. See 11.3, RETINAL DETACHMENT.
- Retinal artery occlusion: Retinal whitening along the distribution of an artery. See 11.6, CENTRAL RETINAL ARTERY OCCLUSION and 11.7, BRANCH RETINAL ARTERY OCCLUSION.
- White without pressure: Common benign peripheral retinal finding. May be associated with a prominent vitreous base.
- Myelinated nerve fiber layer: Develops postnatally (see Figure 11.5.2).
- Chorioretinitis sclopetaria: Bare sclera visible through retinal and choroidal rupture on dilated examination. See 3.19, CHORIORETINITIS SCLOPETARIA.
Workup
Complete ophthalmic evaluation, including dilated fundus examination. Scleral depression is performed except when a ruptured globe, hyphema, microhyphema, or iritis is present. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) shows ellipsoid zone disruption.
Treatment
No treatment is required because this condition is self-limited. Some patients with foveal involvement may be left with chronic visual impairment and RPE atrophy or hyperpigmentation on fundus examination.
Follow Up
Dilated fundus examination is repeated in 1 to 2 weeks. Patients are instructed to return sooner if retinal detachment symptoms are experienced (see 11.3, RETINAL DETACHMENT).