There are a number of alternative head neck positioning techniques that can be performed to improve visualization of the vocal cords during direct laryngoscopy. They include the:
- Sniffing position
- Neutral “in-line” position
- Ramped position
- Beach chair position
- “Sniffing” position is generally thought to be the best position for a patient in preparation for intubation airway management. Ivan Magill, who first proposed the position its definition, described it as somebody “sniffing the morning air” or “drinking a pint of beer.”
- Main advantages: Optimizes airway patency facilitates mask ventilation. Provides good exposure of the glottis in most adult subjects facilitates intubation of the trachea.
- Studies have shown conflicting evidence of its efficacy compared to other combinations of extension flexion of the upper lower cervical spine atlanto-occipital joint. Results conclusions appear to be dependent on the type of population investigated, the endpoints of the studies (easiness of visualization as opposed to easiness of intubation), the experience of the providers, the type of blades utilized.
- Although no univocal conclusion has been reached so far, the sniffing position is most likely a very reasonable “starting point” in preparation for laryngoscopy in the majority of adult patients. Additionally, it may occasionally require adjustments to improve glottis visualization, depending on an individual patient's variability.
- Neutral “in-line” position is the term used to define the cervical spine head alignment in the natural position assumed while supine. There is no head elevation, cervical spine flexion, or extension.
- Main advantages: Provides the best axes alignment for children infants. Avoids further injury or potential injury in patients with a traumatized cervical spine or at risk for such conditions, respectively.
- Disadvantages: Glottis exposure with conventional direct laryngoscopy can be suboptimal in most adults.
- “Ramped” position may be achieved by placing blankets or other specifically manufactured devices underneath the upper body head of the patient.
- Main advantages: Facilitated ventilation visualization of the glottis. Fat tissue at the level of the neck chest is favorably displaced by gravity, can aid with maneuvering the laryngoscope blade hle.
- Beach chair position describes the elevation of the OR bed to 45°.
- Main advantages: Offers optimal airway patency in conditions in which there is a risk of airway collapse obstruction with the patient in the supine position.
- Some anaesthetists advocate that even a 25° “back-up” position of the OR bed offers significant improvement of the laryngeal view compared to the classical supine position, consider this a valuable alternative to the “ramped position.”
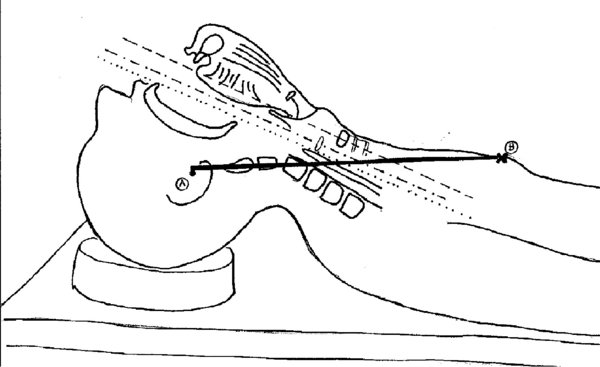
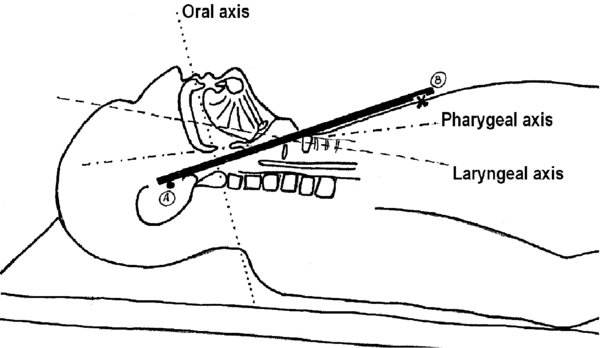
- Sniffing position: Following the observations of Magill, Bannister Macbeth first studied the angles of the oral, pharyngeal, laryngeal axes with the head in different positions. Their aim was to identify the best possible alignment of the 3 axes for the purpose of exposing the glottis facilitating endotracheal tube insertion with direct laryngoscopy.
- In the studies by Bannister Macbeth, the key components to optimal alignment were identified as: Flexion of the lower cervical spine, extension of the upper cervical spine, extension of the atlanto-occipital joint (same as “sniffing position” of Magill).
The external lmarks used were: The position of the chin, the angle of the mible with respect to the OR table, the position of the ears anterior to (or at level with) the sternum. These positions were noted correlated with optimal exposure of the glottis (Figure 1). Although in reality the perfect alignment of these axes does not seem to be achieved, as shown in recent MRI studies, this still seems to be the position that offers the best approximation to the illustrated “ideal alignment.”
FIGURE 1. “Sniffing position (1).”
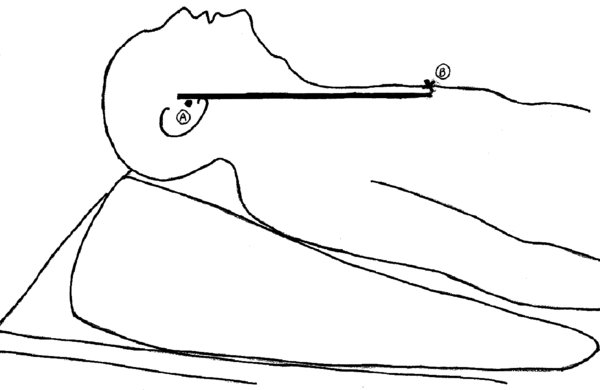
Neutral position: There is no elevation of the head compared to the rest of the body, the cervical spine rests in its natural position without being flexed or extended. In this position the oral, pharyngeal, laryngeal axes are not aligned.
FIGURE 2. Neutral “in-line” position.
There are 3 distinct axes (1).
Ramped position: The presence of a “wedge” underneath the upper body of the patient creates a horizontal alignment between the external auditory meatus the sternal notch. The aim is to achieve in obese patients the same “best alignment” of the 3 axes (oral, pharyngeal, laryngeal) that is reached with the sniffing position in nonobese patients.
FIGURE 3. Ramped position (1).
Beach chair position: The patient's head is in line with the anesthesia provider's xiphoid process. In this position airway patency is maintained better than in the supine position access to the airway by the anesthesia provider is still relatively easy. The provider may be on a step at an angle of the backrest to facilitate direct laryngoscopy manual bag-mask ventilation.
FIGURE 4. Beach chair position (1).
- The presence of medical conditions that alter the patient's anatomy /or the body habitus may significantly influence the choice of the appropriate position to secure the airway.
- Obese patients may benefit from a “ramped,” “beach chair,” or other “back-up” position to optimize glottis exposure.
- Known or suspected cervical spine injury patients are at risk of spinal cord lesions if positioned in the “sniffing position.” Neutral position with “in-line” manual stabilization techniques /or awake fiberoptic technique is recommended for these patients.
- In rheumatoid arthritis patients, anterior atlantoaxial subluxation displacement or fracture of the odontoid process may occur in the “sniffing position.” Extreme caution is recommended with any movement of the cervical spine during intubation.
- Scoliosis previous cervical spine surgery may alter neck mobility prevent optimal positioning for laryngoscopy.
- Conditions affecting the ability of the patient to maintain airway patency, such as the presence of extrinsic or intrinsic obstruction of the upper airway, may require the use of alternative techniques for intubation (e.g., fiberoptic-assisted intubation in the sitting or beach chair position with the patient spontaneously breathing).
Pediatric Considerations
| In infants small children, the prominence of the occiput in relation to the body results in slight neck flexion when the child is supine, , according to some experts, head elevation is not required to obtain optimal positioning for direct laryngoscopy. |
| Moderate head flexion may facilitate nasotracheal intubation in infants young children. |
| Overall there is substantial lack of agreement among experts on the best position for direct laryngoscopy in young children. |
| Down syndrome other congenital syndromes associated with craniofacial anomalies require special attention in planning for laryngoscopy intubation. |
- The choice of one specific position over another may have a critical impact on intubation success rate /or maintenance of adequate oxygenation while managing the airway. It is critical to identify patients who may require airway management in the ramped, beach chair, or “back-up” position (high risk of airway obstruction in the supine position) patients who require “in-line” stabilization in the neutral position (unstable cervical spine). It is also important to be able to recognize anatomical anomalies/changes that may require adjustments of the head neck position in order to obtain better access to the airway for intubation /or ventilation. While no predefined formula exists to help in any given condition, attention to this matter careful consideration of alternative positioning is an important component of a successful strategy for airway management.
- Non-pathological modifications of the body habitus must not be disregarded when planning for direct laryngoscopy positioning. Certain hairdos may affect the possibility to appropriately extend the superior cervical spine the atlanto-occipital joint (e.g., large mass of thick hair pulled up at the back of the head or hair that is worked into firm braids).