Description
- Diastole describes cardiac chamber relaxation filling with blood; it is followed by systole, a period of contraction.
- Ventricular diastole encompasses more than half the time of the cardiac cycle consists of 4 phases:
- Isovolumic relaxation
- Rapid early filling
- Diastasis
- Atrial contraction
- Active relaxation at the molecular level:
- At the cellular level, diastole starts when ATP is hydrolyzed actin–myosin cross-bridges unlink.
- This is associated with decreases in cytoplasmic calcium dissociation of calcium from troponin.
- Calcium sequestration into the SR is accomplished by 2 energy-consuming receptors: The calcium adenosine triphosphate pump (SERCA-2) sodium–calcium exchanger.
- The sarcomere rapidly returns to resting length under normal circumstances. However, when energy supplies are diminished, the inability to sequester calcium can impair relaxation.
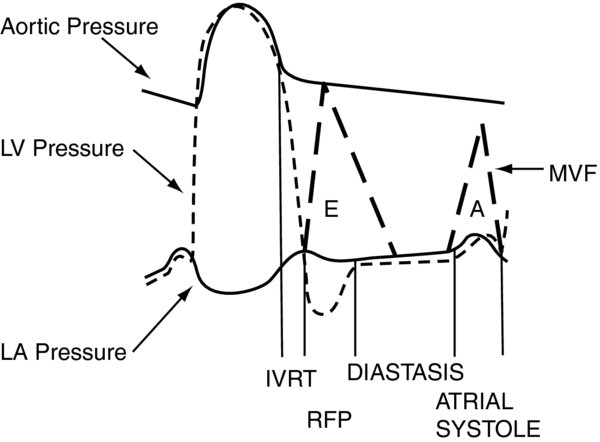
- Valves, volume, pressure during the 4 stages of diastole:
- Isovolumic relaxation time (IVRT):
- Valves: Tricuspid/pulmonic on the right side of the heart the mitral/aortic on the left side of the heart are closed. Of note, the electromechanical onset of diastole (beginning of relaxation) occurs even while the ventricle is ejecting blood (aortic valve open). When the ventricular pressures drop below the aortic pressures, the aortic valve closes IVRT begins.
- Ventricular volume: No change
- Ventricular pressure: Decreases exponentially
- Rapid early filling:
- Valves: Begins when the tricuspid on the right the mitral valve on the left open
- Ventricular volume: Accounts for the majority of ventricular filling (up to 80% of the total stroke volume)
- Ventricular pressure: Initially, there is little to no change with filling. Patients with decreased compliance (e.g., fibrosis, ischemia, diastolic dysfunction) will have a greater increase for a given volume (may also impair this passive filling process).
- Diastasis: Phase can disappear during tachycardia.
- Valves: Tricuspid mitral valves remain open; aortic pulmonic valves are closed.
- Ventricle volume: Remains approximately the same as at the end of the rapid early filling phase
- Ventricle pressure: Atrial ventricular pressures equalize
- Atrial contraction:
- Valves: Tricuspid mitral valve open
- Ventricle volume: The contribution of the “atrial kick” accounts for 15–25% of the stroke volume.
- Ventricle pressure: Creates a positive pressure gradient across the tricuspid mitral valve
- Isovolumic relaxation time (IVRT):
- Pressure–volume loops can aid with the assessment of viscoelastic properties of the ventricle. As described above, during passive filling, the slope is relatively flat; it begins to increase as the ventricle fills.
The heart consists of 2 atria 2 ventricles that circulate blood in series.
- The right left ventricles differ in their shape size, as well as the pressure against which they contract (afterload).
- Right ventricle: Pumps through the low-resistance pulmonary circulation. It is crescent-shaped with an inflow outflow region that contract sequentially to eject blood into the low-pressure pulmonary circulation.
- Left ventricle: Pumps through the systemic circulation. It is ellipsoidal in shape with the muscle fibers arranged longitudinally in the subepicardium subendocardial layers, circumferentially in between these 2 layers. The LV ejects blood with a corkscrew type of motion with the apex moving towards the base. Wall motion of regions supplied by branches of the coronary artery can be individually assessed semi-quantitatively by echocardiography.
Physiology/Pathophysiology
- Factors that can affect the passive pressure–volume properties:
- LV chamber volume: Increases in preload (LV end diastolic volume) from volume overload or decreased forward flow move the pressure–volume curve rightwards. This results in smaller changes in volume will have a large change in pressure (steeper slope).
- Composition of the LV wall (endocardium myocardium): Hypertrophy of muscle, post-ischemic scarring, fibrosis, edema, amyloid deposition, hemosiderin can “stiffen” the wall decrease compliance.
- Extrinsic factors on the ventricle: Pericardial disease, overdistention of the contralateral ventricle, increased airway or pleural pressure, tumors, surgical compression can decrease LV compliance.
- Distensibility/elasticity: Active elasticity of the LV wall is a function of residual cross-bridge activation sarcomere contraction. This potential energy acts as a recoiling force that restores the myocardium to its resting configuration.
- Diastolic heart failure (DHF)
- Definitions
- ACC/AHA criteria: Typical signs symptoms of heart failure; normal LV ejection fraction (>50%); failure not explained by valvular abnormality
- The European Society of Cardiology. Includes additional criteria of evidence of dysfunction through invasive measurements (LVEDP, PCWP >16 mm Hg) or echocardiogram parameters.
- Mechanism is multifactorial poorly understood. It can result from either:
- Intrinsic: Factors affecting ventricular muscle including myocardial relaxation coronary turgor
- Intrinsic factors affecting external compression of the LV including RV pressure or volume overload, pericardial disease, pleural mediastinal pressure, atrial contraction
- Linking etiology with cellular mechanisms
- Aging is associated with prolonged isovolumic relaxation altered calcium homeostasis as well as interstitial fibrosis increased cross-linking of collagen that can cause LV stiffness.
- Chronic hypertension increases myocardial work/tension is often compensated for with muscle hypertrophy.
- Diabetes is associated with myocyte hypertrophy interstitial fibrosis with microvascular disease.
- Definitions
- Atrial kick: The stroke volume decreases in the absence of an atrial contraction; this can be seen with atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, low atrial rhythms, or junctional rhythms. In patients with decreased ventricular compliance, where passive filling is already decreased, the stroke volume becomes more dependent on the atrial “kick.”
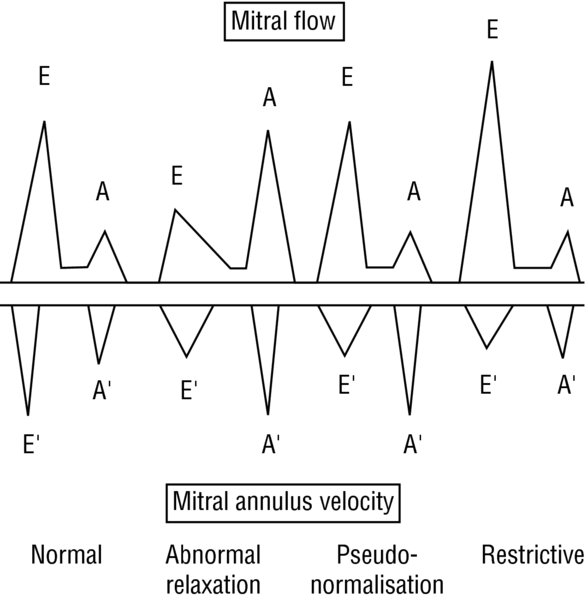
- Echocardiogram: LV diastolic function is assessed via pulse wave Doppler (PWD) assessment through the mitral valve. A mid-esophageal 4-chamber view allows the beam to be aligned parallel to blood flow thus provides the most ideal imaging of flow velocity. The transmitral pattern is composed of the:
- “E” wave: Represents the rapid filling phase
- “A” wave: Represents atrial contraction. The wave is approximately 1/3 to 1/2 the size of the E wave.
- Deceleration time (DT): Time it takes for the E wave velocity to become zero. A time 220 ms represents good LV relaxation a rapid decline in ventricular pressure.
- PWD classification of diastolic dysfunction
- Impaired relaxation (Grade I): This initial pattern of dysfunction is seen early in the course of hypertension, myocardial ischemia, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
- Small “E” wave
- Large “A” wave
- E/A ratio 1
- Prolonged DT (>240 ms)
- Pseudo-normal pattern (Grade II): As the disease process progresses, the LA pressure , hence, LA–LV gradient increases. This results in a “normal” appearing pattern. In order to distinguish true normal from pseudonormal, maneuvers to decrease preload (e.g., Valsalva, nitroglycerin, etc.) can be applied to unmask a small “E” wave, large “A” wave, prolonged DT time.
- Normal appearing “E” wave: The increased size compared to Grade I reflects the increase in passive filling flow from the increased LA–LV gradient.
- Normal appearing “A” wave: The decreased size compared to Grade I reflects the minimal contribution of the atrial contraction.
- E/A ratio >1
- DT of 160–240 ms: The shortened time results from rapid equilibration pressure between the LA LV.
- Restrictive pattern (Grade III IV) can be seen in decompensated heart failure, severe coronary artery disease, constrictive pericarditis, severe aortic mitral insufficiency. They result in LV filling occurring primarily in early diastole.
- Very large “E” wave
- Small “A” wave
- E/A ratio >2
- Shortened DT interval from rapid rise in the LV diastolic pressure time to diastasis
- Impaired relaxation (Grade I): This initial pattern of dysfunction is seen early in the course of hypertension, myocardial ischemia, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Laplace's law: T = (P × r)/(2 × h), where P is the intraventricular pressure, r is the ventricular radius, h is wall thickness.
FIGURE 1. The 4 phases of diastole.
IVRT begins with aortic valve closure ends with mitral valve opening. RFP—Rapid Early Filling. MVF—Mitral Valve Flow.
FIGURE 2. Doppler E A waves from echocardiogram are superimposed.
(Reproduced from Reference 3, permission requested pending).