- Unless otherwise specified, preload describes the volume of blood distending the left ventricle at the end of diastole (i.e., end of the ventricular filling phase), also known as left ventricular end-diastolic volume (LVEDV). The concept of preload can also be applied to any chamber of the heart
- Direct assessment of cardiac preload requires measurement of the blood volume within the reference chamber. This is generally done via echocardiography which can be performed intraoperatively but is also possible by MRI, CT, radionuclide angiography, and cardiac catheterization. In the perioperative period, preload is often assessed indirectly via interpretation of static cardiac filling pressures and/or the dynamic relationship of filling pressures on cardiac output.
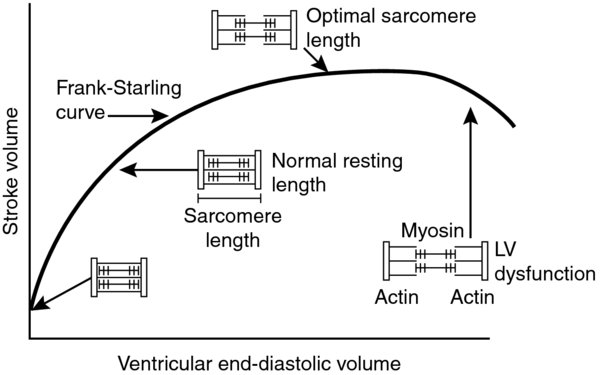
Static measures of preload: Cardiac preload is a major determinant of cardiac performance via the Frank–Starling mechanism. The curvilinear Frank–Starling curve demonstrates the effect of preload versus contractility (as measured by stroke volume). Until the chamber is grossly overdistended, increasing preload [end-diastolic volume (EDV)] will increase the intrinsic strength of the systolic contraction and increase the stroke volume.
FIGURE 1. Frank–Starling curve: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2220/
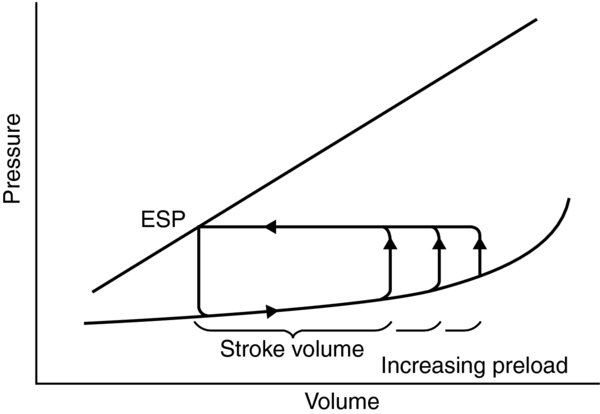
FIGURE 2. Stroke volume preload dependence
- Ventricular preload (filling volume) is increased by: Increased filling pressure (increased total blood volume, decreased venous compliance, or gravity/Trendelenburg position) or increased myocardial compliance. Chamber compliance determines how much the EDV increases relative to the increased pressure.
- Ventricular preload is decreased by: Hypovolemia (dehydration, hemorrhage), impaired atrial contraction (loss of ‘atrial kick’), increased heart rate (decreased filling time), decreased afterload (smaller residual end-systolic volume), and diastolic heart failure (impaired relaxation/compliance).
- Although pressure measurements are commonly used as surrogate measures of preload (EDV), it is important to note that the pressure–volume relationship is not linear and is often dynamic.
- In the absence of significant lung disease or mitral valve disease, pulmonary artery occlusion pressure (PAOP) approximates LVEDP; LVEDP is assumed
 LVEDV
LVEDV - In the absence of tricuspid valve pathology, central venous pressure (CVP) or right atrial pressure (RAP) approximates right ventricular end-diastolic pressure (RVEDP); RVEDP is assumed
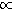 RVEDV
RVEDV - In the absence of significant right heart pathology, pulmonary disease, or mitral valve disease, adequate RVEDV (as suggested by its CVP surrogate) is also assumed to translate into adequate LVEDV (preload for the systemic circulation).
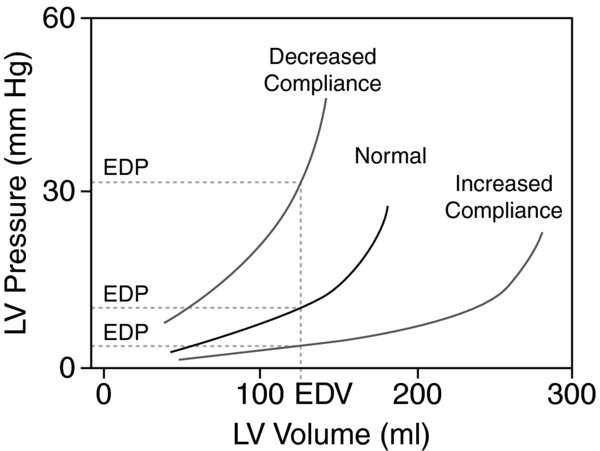
Surrogate pressure measurements may not begin to increase from near zero (slope of pressure–volume relationship is near zero) until ventricular volumes are above 40–50 mL. A curvilinear increase in filling pressure per unit preload volume is then seen until ventricular volumes near their end-diastolic capacity, where the pressure–volume slope increases (this slope assumes a more linear relationship if the pericardium is removed).
FIGURE 3. Pressure-volume relationship of the left ventricle. http://www.cvphysiology.com/Cardiac%20Function/CF014.htm
- In the absence of significant lung disease or mitral valve disease, pulmonary artery occlusion pressure (PAOP) approximates LVEDP; LVEDP is assumed
- Dynamic measures of preload: Trends indicating the change in stroke volume or blood pressure over different preload conditions are more useful indicators of ongoing volume responsiveness than static pressure surrogates.
- When total blood volume is low compared to vascular capacitance (relative hypovolemia with low preload), an adequate fluid challenge (>10 mL/kg of crystalloid given in <30 min) may provide only a transient increase in blood pressure and little (<3 cm H2O) sustained increase in CVP/PAOP
- When total blood volume is approaching vascular capacity and cardiac preload is still low, an adequate fluid challenge should provide a sustained blood pressure increase and a sustained (>3 cm H2O) increase in CVP/PAOP.
- When total blood volume is in excess and cardiac preload reserve has been exhausted, ongoing fluid challenges will not further increase blood pressure/cardiac output, but significant sustained CVP/POAP increases will still be seen.
- Passive leg raises or Trendelenburg positioning may provide the patient with a significant enough "volume challenge" to determine volume responsiveness.
- Under the conditions of regular controlled positive pressure ventilation (>8 mL/kg tidal volumes) and regular sinus heart rhythm, heart–lung interactions will cause cardiac preload conditions to change throughout the respiratory cycle.
- Increased systolic pressure, pulse pressure, and stroke volume variations indicate increased cardiac preload dependence and can predict ongoing fluid responsiveness.
- Depending on the non-invasive cardiac output measuring device and variable selected, a variation of >11–13% of stroke volume often predicts volume responsiveness (1) [A].
- Respiratory variation of the pulse oximetry plethysmograph of >14% may also suggest volume responsiveness (2) [B].
- Aortic blood flow velocity variation >12% (measured by echocardiography or esophageal Doppler) is similarly highly predictive of volume responsiveness (3) [B].
- Looking at the venous system via bedside ultrasound, an inferior vena cava (IVC) distensibility index >12% predicts volume responsiveness (4) [B]. IVC engorgement occurs as positive pressure ventilation inhibits blood return to the right heart.
- Increased systolic pressure, pulse pressure, and stroke volume variations indicate increased cardiac preload dependence and can predict ongoing fluid responsiveness.
- In spontaneously ventilating patients, IVC collapse of >50% suggests a CVP <10 and predicts volume responsiveness.
- Microscopically, preload describes the sarcomere length related to myocyte stretching.
- Macroscopically, preload is the three-dimensional volume of blood within the chamber that is responsible for the one-dimensional sarcomere length of the stretched myocytes.
Pregnancy Considerations
| To avoid IVC compression by the uterus, left uterine displacement (rotation of hips/torso towards left side) is suggested when a parturient (of >24 weeks gestation) would otherwise be positioned supine. |
| Uterine compression of the IVC may impair venous return and decrease preload, resulting in up to a 30% reduction of cardiac output. |
- Volume overload. Upon gross overdistention of the chamber, microscopic myofibrils (myosin and actin) are stretched beyond their ability to optimally overlap, decreasing their strength/contractility and heart failure ensues (Figure 1).
- Diastolic dysfunction results in increased filling pressures as a compensatory mechanism to maintain adequate/minimal EDV. Such compensated patients often appear more sensitive to filling pressure/volume decreases and are relatively "preload dependent."
- Myocardial ischemia. Filling of a cardiac chamber during diastole involves both the active (early) relaxation by the myocytes and the passive compliance of chamber's wall. Active relaxation of a cardiac chamber is decreased during myocardial ischemia. Relaxation (diastolic) abnormalities occur in the ischemic tissue before contraction (systolic) dysfunction is seen. Impaired active relaxation (during ischemia) will result in reduced ventricular filling during diastole, contributing to the appearance of decreased compliance (decreased ventricular volume for same filling pressure).
- Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH). As the ventricular wall thickens, it becomes less compliant. LVH can develop with:
- Increased afterload: Hypertension, morbid obesity, and aortic stenosis that result in a chronic increase in work.
- Reduced compliance: Infiltrative diseases such as amyloidosis or cardiac tumors where there is an increase in myocardial stiffness.
- Rhythm disturbances (tachycardia, heart block, atrial fibrillation, or atrial flutter) may impair filling by decreasing coordinated active relaxation or by simply decreasing the total filling time.
- Tricuspid stenosis and mitral stenosis result in increased measured CVP and PAOP, respectively, while RVEDP and LVEDP may remain normal (valvular stenosis creates a pressure gradient and violates the assumptions required for CVP and PAOP approximate RVEDP and LVEDP, respectively).
- External compression from pericardial effusion, positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), tension pneumothorax, pleural effusions, or greatly increased abdominal pressures may reduce passive ventricular compliance.
- Intraventricular filling defects (tumors and clots) and septal shifts causing ventricular interdependence (severe pulmonary hypertension, high levels of PEEP, and RV infarction) may restrict diastolic filling of cardiac chambers.
- Surrogate filling pressures (CVP and PAOP) cannot reliably discern diastolic dysfunction from systolic dysfunction. In several studies in critically ill patients, volume assessment via transesophageal echocardiography disagreed with static pulmonary artery catheter pressure assessments in up to 55% of patients and significantly altered medical management in 32–44% of those patients (5) [B].
- Volume responsiveness refers to the ability of an increase in preload (volume challenge) to produce a clinically significant increase in stroke volume (resulting in increased blood pressure and cardiac output).
- Ongoing volume responsiveness suggests that the LV is still on the upslope of the Frank–Starling curve (increased LVEDP generates the expected increased ventricular contractility).
- Lack of volume responsiveness suggests that the LV has "fallen off" the Frank–Starling curve (meaning increased LVEDP no longer generates increased contractility).
- Many pathophysiologic processes disrupt the normal relationship between measured filling pressures and actual preload volumes, making appropriate interpretation of filling pressures difficult.