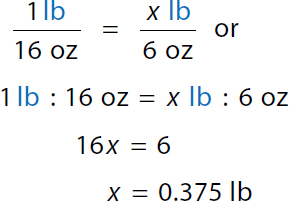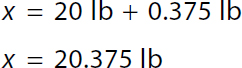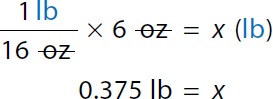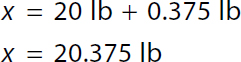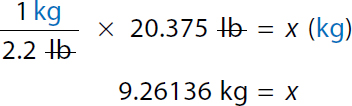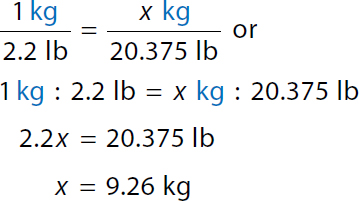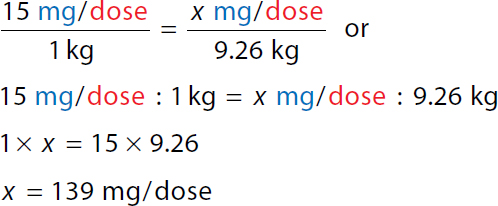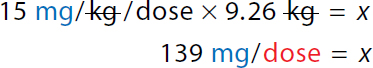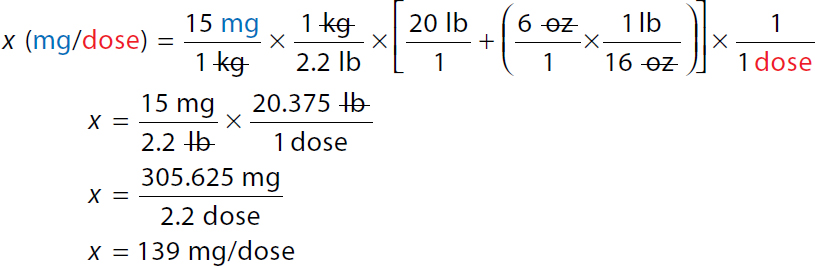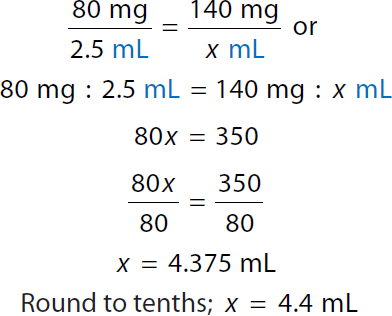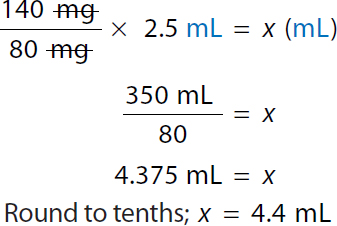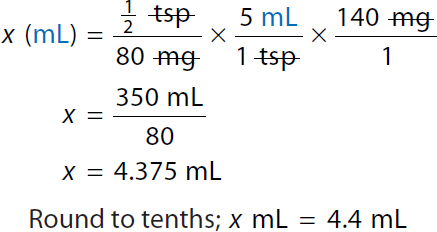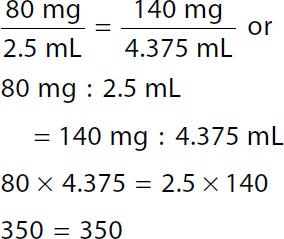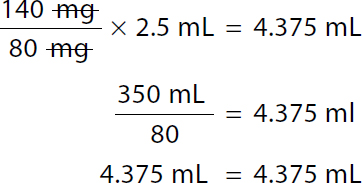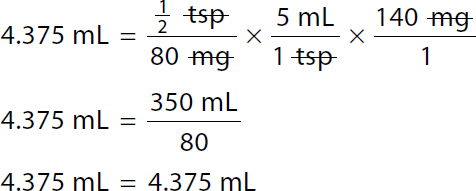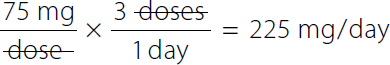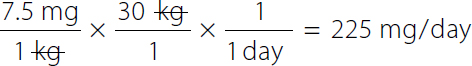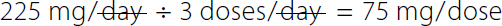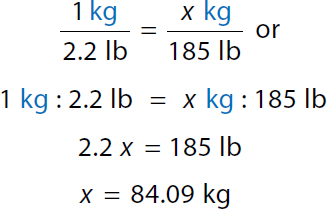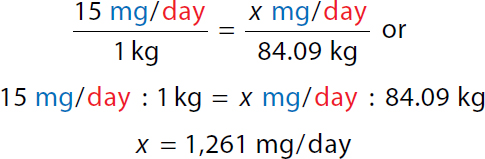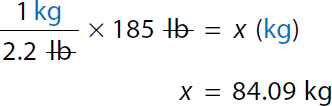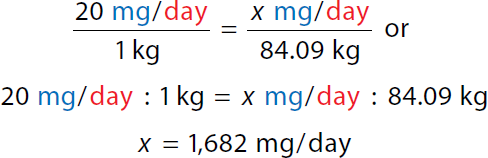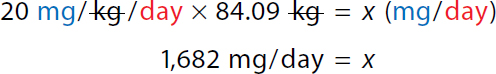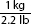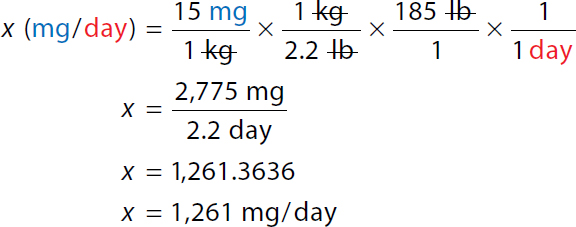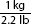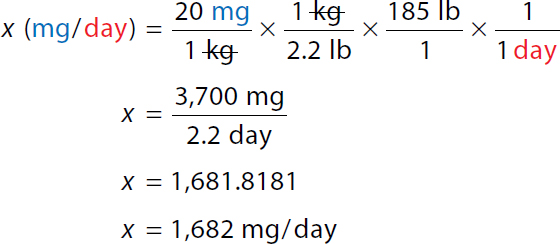After calculating a safe dose, the nurse compares the ordered dose to the calculated safe dose. If the ordered dose matches the safe dose or falls within the safe dose range, the nurse can proceed with medication administration. If the ordered dose does not match the safe (recommended) dose or does not fall within the (recommended) SDR, the nurse should not administer the medication but should contact the authorized prescriber right away.
Example 1: Determine if the order is safe; if it is safe, calculate the amount, in mL, to administer.
Order: acetaminophen 140 mg PO q4h prn fever greater than 38.5°C for a 20 lb 6 oz child
Reference: Recommended dose of acetaminophen is 15 mg/kg per dose.
Supply: acetaminophen 80 mg/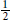 teaspoon (see Figure 12-3)
teaspoon (see Figure 12-3)
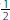 tsp.
tsp.
A label of the label of infants' acetaminophen.
Text on the label reads, For Children. Acetaminophen. Oral Suspension. Pain Reliever-Fever Reducer. Half fluid ounces, 15 milliliters. 160 milligrams per 5 milliliters. N D C 50580 191 05. R x only.
Step 1: Convert weight to kg using the conversion factors 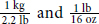 .
.
Step 2: Calculate the safe dose.
Step 3: Determine whether the ordered dose is safe by comparing it to the safe dose.
Step 4: Calculate the amount to administer or contact the prescriber if the ordered dose is not safe.
Ratio-Proportion | Formula Method |
|---|---|
Step 1a: Convert oz to lb
1 pound over 16 ounces equals x pound over 6 ounces. A ratio of 1 pound to 16 ounces equals a ratio of x pound to 6 ounces. 16 x equals 6. x equals 0.375 pounds. Step 1b: Combine partial pounds with whole pounds
x equals 20 pounds plus 0.375 pounds. x equals 20.375 pounds. | Step 1a: Convert oz to lb
1 pound over 16 ounces times 6 ounces equals x pound. 0.375 pound equals x. Step 1b: Combine partial pounds with whole pounds
x equals 20 pounds plus 0.375 pounds. x equals 20.375 pounds. Step 1c: Convert 20.375 lb to kg
1 kilogram over 2.2 pounds times 20.375 pounds equals x kilogram. Both the numerator and denominator pound canceled each other. 9.26136 kilogram equals x. |
Step 1c: Convert 20.375 lb to kg
1 kilogram over 2.2 pound equals x kilogram over 20.375 pound. A ratio of 1 kilogram to 2.2 pounds equals x kilogram to 20.375 pounds. 2.2 x equals 20.375 pounds. x equals 9.26 kilograms. Step 2: Calculate SSD
To calculate the value of x. 15 milligrams over dose all over 1 kilogram equals x milligrams over dose all over 9.26 kilogram. A ratio of 15 milligrams over dose to 1 kilogram equals a ratio of x milligrams over dose to 9.26 kilograms. 1-time x equals 15 times 9.26. x equals 139 milligrams over dose. | Step 2: Calculate SSD
15 milligrams over kilogram over dose times 9.26 kilogram equals x. On the left-hand side, The numerator and denominator kilogram canceled each other. 139 milligrams over dose equals x. |
Steps 1a, 1b, 1c, and 2 are combined
A calculation of dimensional analysis for supply of 160 milligrams over 5 milliliters. Calculation reads, x milligram over dose equals 15 milligrams over 1 kilogram times 1 kilogram over 2.2 pound times open square bracket 20 pounds over 1 plus open parenthesis 6 ounces over 1 times 1 pound over 16 ounces close parenthesis close square bracket times 1 over 1 dose. Both the numerator and denominator kilogram and ounce are canceled each other. x equals 15 milligrams over 2.2 pounds times 20.375 pounds over 1 dose. Both the numerator and denominator pound canceled each other. x equals 305.625 milligrams over 2.2 doses. x equals 139 milligrams over dose. | |
Step 3: Compare the ordered dose to the recommended dose.
When there is only a slight difference between the ordered dose, 140 mg, and the calculated safe dose, 139 mg, it is usually acceptable to proceed with medication administration; however, to err on the side of caution, the nurse should contact the prescriber when comparing the ordered dose to the safe calculated dose.
Step 4: Because the ordered dose is safe, the nurse can now use the CASE approach to determine the amount to administer.
C:Convert—Because the order and the supply are both in milligrams, no conversion is needed for the amount. Because the supply volume is given in teaspoons (tsp) and the answer requested is mL, convert 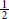 tsp to 2.5 mL; for dimensional analysis, use the conversion factor 1 tsp/5 mL.
tsp to 2.5 mL; for dimensional analysis, use the conversion factor 1 tsp/5 mL.
A:Approximate—The ordered dose, 140 mg, is almost two times the supply amount of 80 mg, so almost two times the supply volume of 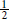 tsp (i.e., almost 1 tsp [5 mL]) will be needed to administer the ordered dose.
tsp (i.e., almost 1 tsp [5 mL]) will be needed to administer the ordered dose.
S:Solve
Ratio-Proportion | Formula Method |
|---|---|
A calculation of ratio proportion method for ordered dose 140 milligrams. Calculation reads, 80 milligrams over 2.5 milliliters equals 140 milligrams over x milliliters. A ratio of 80 milligrams to 2.5 milliliters equals a ratio of 140 milligrams to x milliliters. 80 x equals 350. 80 x over 80 equals 350 over 80. x equals 4.375 milliliters. Round to tenths. x equals 4.4 milliliters. |
A calculation of formula method for ordered dose 140 milligrams. Calculation reads, 140 milligrams over 80 milligrams times 2.5 milliliters equals x milliliters. Both the numerator and denominator milligrams canceled each other. 350 milliliters over 80 equals x. 4.375 milliliters equals x. Round to tenths. x equals 4.4 milliliters. |
A calculation of dimensional analysis for an ordered dose of 140 milligrams. Calculation reads x milliliters equals half teaspoons over 80 milligrams times 5 milliliters over 1 teaspoon times 140 milligrams over 1. Both the numerator and denominator teaspoon and milligram are canceled each other. x equals 350 milliliters over 80. x equals 4.375 milliliters. Round to tenths. x milliliters equals 4.4 milliliters. | |
E:Evaluate
Ratio-Proportion | Formula Method |
|---|---|
A calculation of ratio proportion evaluation for ordered dose 140 milligrams. Calculation reads, 80 milligrams over 2.5 milliliters equals 140 milligrams over 4.375 milliliters or. A ratio of 80 milligrams to 2.5 milliliters. Equals a ratio of 140 milligrams to 4.375 milliliters. 80 times 4.375 equals 2.5 times 140. 350 equals 350. |
A calculation of formula evaluation for ordered dose 140 milligrams. Calculation reads, 140 milligrams over 80 milligrams times 2.5 milliliters equals 4.375 milliliters. Both the numerator and denominator milligram canceled each other. 350 milliliters over 80 equals 4.375 milliliters. 4.375 milliliters equals 4.375 milliliters. |
Dimensional Analysis | |
A calculation of evaluation analysis for an ordered dose of 140 milligrams. Calculation reads, 4.375 milliliters equals half teaspoons all over 80 milligrams times 5 milliliters over 1 teaspoon times 140 milligrams over 1. Both the numerator and denominator teaspoon and milligram are canceled each other. 4.375 milliliters equals 350 milliliters over 80. 4.375 milliliters equals 4.375 milliliters. | |
Because the calculated volume accurately completes the equation and is consistent with the approximated volume, the answer, 4.4 mL, is confirmed.
Warning!Example 2: Determine if the order is safe; if it is safe, calculate the amount, in mL, to administer.
Order: erythromycin lactobionate 250 mg IV q6h for an adult weighing 185 lb
Reference: Recommended daily dosage of erythromycin lactobionate for adult patients is 15–20 mg/kg/day to be administered in 4 divided doses.
Supply: See Figure 12-4.
A label of Erythromycin Lactobionate 4 U S P for injection. Text on the label reads, N D C 0703 0956 03. R x only. Erythromycin activity. 500 milligrams per vial. Sterile powder.
Ratio-Proportion | Formula Method |
|---|---|
Step 1: Convert lb to kg
Calculation reads, 1 kilogram over 2.2 pounds equals x kilogram over 185 pounds or. A ratio of 1 kilogram to 2.2 pounds equals a ratio of x kilogram to 185 pounds. 2.2 x equals 185 pounds. x equals 84.09 kilograms. Step 2a: Calculate minimum daily dose
A calculation for the minimum daily dose by ratio proportion for special patients. Calculation reads, 15 milligrams over day all over 1 kilogram equals x milligrams over day all over 84.09 kilograms or. A ratio of 15 milligrams over day to 1 kilogram equals a ratio of x milligrams over day to 84.09 kilograms. x equals 1261 milligrams over day. | Step 1: Convert lb to kg
A calculation for the maximum daily dose by ratio proportion for special patients. Calculation reads, 20 milligrams over day all over 1 kilogram equals x milligrams over day all over 84.09 kilograms or. A ratio of 20 milligrams over day to 1 kilogram equals a ratio of x milligrams over day to 84.09 kilograms. x equals 1682 milligrams over day. Step 2a: Calculate minimum daily dose
Calculation reads, 15 milligrams over kilogram over day times 84.09 kilograms equals x milligrams over day. Both the numerator and denominator kilogram canceled each other. 1261 milligrams over day equals x. |
Step 2b: Calculate maximum daily dose
A calculation for the maximum daily dose by formula method for special patients. Calculation reads, 20 milligrams over day all over 1 kilogram equals x milligrams over day all over 84.09 kilograms or. A ratio of 20 milligrams over day to 1 kilogram equals x milligrams over day to 84.09 kilograms. x equals 1682 milligrams over day. | Step 2b: Calculate maximum daily dose
A calculation for the maximum daily dose using conversion factor 1 kilogram over 2.2 pounds. Calculation reads, x milligrams over day equals 20 milligrams over 1 kilogram times 1 kilogram over 2.2 pounds times 185 pounds over 1 times 1 over 1 day. Both the numerator and denominator kilogram and pound canceled each other. x equals 3700 milligrams over 2.2 days. |
Dimensional Analysis | |
Steps 1 and 2 are combined. Calculate minimum daily dose; use conversion factor
A calculation for the minimum daily dose by dimensional analysis for special patients. Calculation reads, x milligrams over day equals 15 milligrams over 1 kilogram times 1 kilogram over 2.2 pounds times 185 pounds over 1 times 1 over 1 day. Both the numerator and denominator kilogram and pound are canceled each other. x equals 2775 milligrams over 2.2 days. x equals 1261.3636. x equals 1261 milligrams over day. | |
Calculate maximum daily dose; use conversion factor
A Calculation reads, x milligrams over day equals 20 milligrams over 1 kilogram times 1 kilogram. Calculation reads, x milligrams over day equals 20 milligrams over 1 kilogram times 1 kilogram over 2.2 pounds times 185 pounds over 1 times 1 over 1 day. Both the numerator and denominator kilogram and pound canceled each other. x equals 3700 milligrams over 2.2 days. x equals 1681.8181. x equals 1682 milligrams over day. | |
- The minimum daily dose of erythromycin for a 185 lb adult is 1,261 mg per day.
- The maximum daily dose of erythromycin for a 185 lb adult is 1,682 mg per day.
- The safe daily dose range of erythromycin for a 185 lb adult is 1,261 to 1,682 mg per day.
Step 3: Compare the ordered dose to the safe dose.
Because the ordered dose, 250 mg, is to be given four times daily (q6h), the daily dose (4 × 250 mg) would be 1 g or 1,000 mg. Because 1,000 mg per day is outside the safe daily dose range of 1,261 to 1,682 mg, the order is not safe.
Step 4: Because the order is not safe, the nurse will not carry out this drug order but instead will contact the prescriber for a new order.
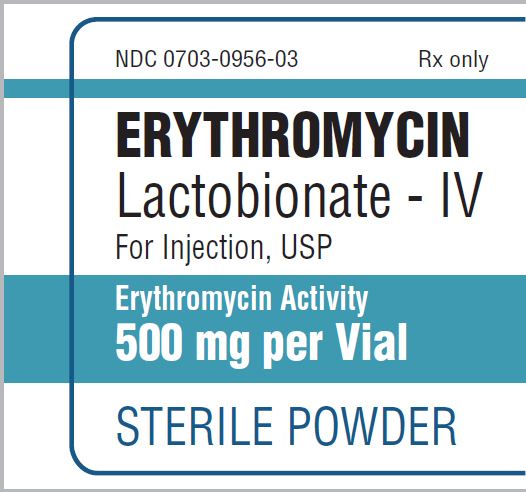
If desired with Example 2, the nurse could calculate the safe single dose of erythromycin and then compare it to the single dose of erythromycin ordered. To determine the safe single dose of erythromycin, the nurse should divide the daily dose by the number of doses per day. Recall that the drug reference states that erythromycin should be given "in 4 divided doses." Therefore, the conversion factor 1 day/4 doses is inserted into the dimensional analysis equation or the recommended daily dose is divided by 4 to determine the safe single dose:
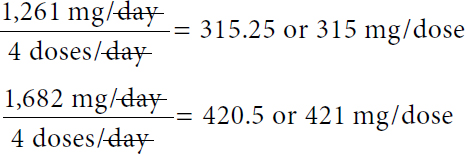
Calculation reads, 1261 milligrams over day all over 4 doses over day equals 315.25 or 315 milligrams over dose. Both the numerator and denominator day canceled each other.
- The minimum single dose of erythromycin for a 185 lb adult is 315 mg per dose.
- The maximum single dose of erythromycin for a 185 lb adult is 421 mg per dose.
- The safe single dose range of erythromycin for a 185 lb adult is 315 to 421 mg per dose.
Because the dose ordered, 250 mg, is outside the safe dose range, the nurse must contact the prescriber for a new order right away.
LEARNING ACTIVITY 12-4 Apply the following orders to a 15 kg child and:
a. Calculate the safe daily dose/dose range.
b. Compare the ordered daily dose to the safe daily dose/dose range.
c. Determine whether the nurse should calculate the amount to administer (for a single dose) or contact the prescriber.
1.Order: oxcarbazepine 75 mg PO bid
Reference: Safe dose of oxcarbazepine is 8–10 mg/kg/day in divided doses q12h.
Supply: See Figure 12-5.

A label of Oxcarbazepine.
Text on the label reads, Oral suspension. 300 milligrams per 5 milliliters. 250 milliliters. Shake well before using. Each 5 milliliter contains 300 milligrams of oxcarbazepine. N D C 0078 0357 52.
2.Order: Zantac 15 mg IV q8h
Reference: Recommended dose of ranitidine is 2–4 mg/kg/day in divided doses q6–8h.
Supply: See Figure 12-6.
A label of Ranitidine. Text on the label reads, Injection U S P. 50 milligrams per 2 milliliters. 10 milliliters. Each milliliter contains 25 milligrams of ranitidine. N D C 55390 616 01.
3.Order: albuterol sulfate 2 mg PO tid
Reference: Recommended pediatric dosage of albuterol sulfate is 0.3 mg/kg/day in three divided doses, not to exceed 2 mg tid.
Supply: See Figure 12-7.

A label of Albuterol Sulfate syrup.
Text on the label reads, 2 milligrams per 5 milliliters. 473 milliliters. Each 5 milliliter or 1 teaspoonful contains albuterol sulfate 2.4 milligrams, equivalent to 2 milligrams of albuterol. Usual Dosage: See package insert for full prescribing information. Store at 20 to 25 degrees Celsius, or 68 to 77 degrees Fahrenheit. See U S P Controlled Room Temperature. This is a bulk package. Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the U S P, with a child-resistant closure, as required. Keep this and all medications out of the reach of children.