Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis

Deep vein thrombosis
Essentials
- As many as half of all cases of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) develop without clinical symptoms, and only pulmonary embolism (PE) prompts diagnostic tests.
- A normal D-dimer test result is enough to rule out DVT when, based on clinical presentation, the probability of DVT is no more than moderate. However, if the likelihood of DVT is clinically high, diagnostic imaging studies are indicated.
- Before treatment is started, a blood sample should be collected for the analysis of blood clotting factors (thrombophilia screening Evaluation of Thrombophilia) if the patient has a positive family history, recurrent or idiopathic (no identified risk factors) thrombosis, massive thrombosis, miscarriage or thrombi affecting both the venous and arterial vessels, or if the patient is young.
- Treatment aims to prevent PE and post-thrombotic syndrome.
- All risk factors, or their absence, must be recorded. They determine the duration of the anticoagulant therapy.
Risk factors
- DVT is rare if no risk factors are present.
- The most important risk factors for DVT are
- previous venous thrombosis or embolism
- severe infection, heart failure
- oral contraceptives
- oestrogen therapy or pregnancy
- immobility (bed rest, flight travel, fractures)
- surgery
- cancer
- inherited thrombophiliaEvaluation of Thrombophilia.
- All risk factors, or their absence, must be recorded. They determine the duration of the anticoagulant therapy (3 months - indefinite).
Clinical assessment
Clinical picture
- Common signs and symptoms associated with lower limb DVT are:
- oedemaLeg Oedema, pain
- dilatation of superficial veins
- Positive Homan's sign (flexion of the ankle causes calf pain).
- As many as half of all cases of DVT develop without clinical symptoms, and only PE prompts diagnostic tests. However, the specificity of the above signs and symptoms is small, particularly when they occur alone Wells Score and D-Dimer in the Diagnosis of Deep Vein Thrombosis.
- In addition to the lower limbs, venous thrombosis may also develop occasionally in
- an upper limb
- the pelvic veins
- association with a central venous catheter
- the right heart chambers
- the portal vein and cerebral venous sinuses.
Assessment of pretest probability
- The scoring of pretest probability of DVT is presented in table T1.
Assessment of pretest probability
| Clinical parameter | Score |
|---|---|
| Active cancer (treatment ongoing, within 6 months or palliative) | 1 |
| Paralysis, paresis or recent plasterimmobilisation of a lower limb | 1 |
| Recently bedridden for longer than 3 days or major surgery within 4 weeks | 1 |
| Localised tenderness along the distribution of the deep venous system | 1 |
| Entire leg swollen | 1 |
| Calfswelling>3 cm compared with the asymptomatic leg (measured 10 cm below the tibial tuberosity) | 1 |
| Pitting oedema (greater in the symptomatic leg) | 1 |
| Collateral superficial veins (non-varicose) | 1 |
| Alternative diagnosis as likely or greater than that of DVT | - 2 |
|
| Wells PS, Anderson DR, Bormanis J et al. Value of assessment of pretest probability of deep-vein thrombosis in clinical management. Lancet 1997;350:1795-8 1 | ||||||||||
| If the D-dimer test is negative and the score < 3, no other investigations are needed. | ||||||||||
If the D-dimer test is positive or the score 3 or higher, compression ultrasonography is indicated.
Investigations
D-dimer
Ultrasonography
Venography
Other laboratory tests
Treatment
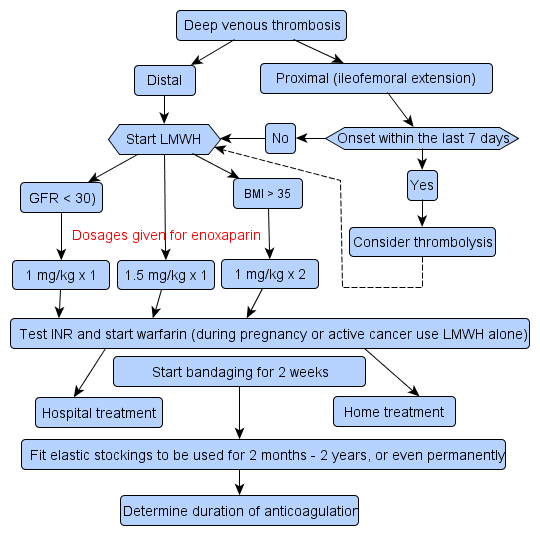
Management in primary care
Anticoagulant therapy: dose and duration
Duration of anticoagulant therapy
Thrombolytic therapy (fibrinolytic therapy)
Surgical treatment
Other treatment
Related resources
| ||||||||||