General assessment of the serum proteins includes measurement of total protein, albumin, globulin, and the albumin-to-globulin (A-G) ratio. Although these tests are being replaced by serum protein electrophoresis (see Chapter 3 - Immunology and Immunologic Testing), they may still be ordered for screening purposes or as components of multitest chemistry profiles, because they provide an overall picture of protein homeostasis.
Several disorders can cause alterations in serum proteins. Those affecting total protein levels are listed in Table 5-3. Albumin levels show less variation. Except for dehydration, exercise, and effects of certain drugs (e.g., gallamine triethiodide [Flaxedil]), elevated albumin levels do not occur. Albumin may be decreased in a number of situations caused, in general, by (1) decreased hepatic synthesis, (2) excessive renal excretion, (3) increased metabolic degradation, and (4) complex combined disorders. Specific problems associated with hypoalbuminemia are listed in Table 5-4.
Globulin levels show more variation than do albumin levels, probably because of the multiple production sites for this protein. Causes of altered globulin levels are listed in Table 5-5 according to the type of globulin affected.
The A-G ratio indicates the balance between total albumin and total globulin and is usually evaluated in relation to the total protein level. A low protein level and a reversed A-G ratio (i.e., decreased albumin and elevated globulins) suggest chronic liver disease. A normal total protein level with a reversed A-G ratio suggests myeloproliferative disease (e.g., leukemia, Hodgkin's disease) or certain chronic infectious diseases (e.g., tuberculosis, chronic hepatitis).
Nursing Care Before the Procedure
Client preparation is the same as that for any test involving collection of a peripheral blood sample (see Appendix I).
- Some laboratories require an 8-hour fast before the test, as well as a low-fat diet for several days before the test, because high serum lipid levels may interfere with accurate testing.
A venipuncture is performed and the sample collected in a red-topped tube. The sample should be handled gently and sent promptly to the laboratory.
Nursing Care After the Procedure
Care and assessment after the procedure are the same as for any study involving collection of a peripheral blood sample. Resume any foods withheld before the test.
- Abnormal values: Note and report increased levels. Assess for symptoms of dehydration that can cause hyperproteinemia such as thirst, dry skin and mucous membranes, or poor skin turgor. Assess fluid loss resulting from vomiting, diarrhea, or renal dysfunction. Note and report decreased levels. Assess in relation to hypoalbuminuria and for edema in serum albumin levels as low as 2.0 to 2.5 g/dL. Assess for causes of hypoalbuminemia such as acute or chronic liver disease or renal dysfunction. Assess for stress, injury, or infection that requires increased protein intake. Prepare for IV administration of albumin replacement in severe conditions. Monitor I&O. Encourage and instruct in increased dietary protein intake.
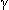 -globulins are provided for comparison purposes.
-globulins are provided for comparison purposes.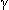 -Globulins
-Globulins 1
1 2
2