Population: Adult men with signs/symptoms of hypogonadism.
Organizations
 Endocrine Society 2018, EAU 2018, AUA 2018, ACP 2020
Endocrine Society 2018, EAU 2018, AUA 2018, ACP 2020
Recommendations
Evaluation
–Evaluate men who have symptoms and signs of androgen deficiency: lethargy, easy fatigue, lack of stamina or endurance; reduced libido, decreased spontaneous erections; male infertility; mood changes; gynecomastia, loss of body hair, small testes; osteopenia/osteoporosis.
–Consider testing testosterone in men with pituitary masses, obesity, metabolic syndrome, moderate-to-severe COPD, infertility, osteoporosis, HIV, DM type 2, or chronic use of corticosteroids and/or opiates. (EAU)
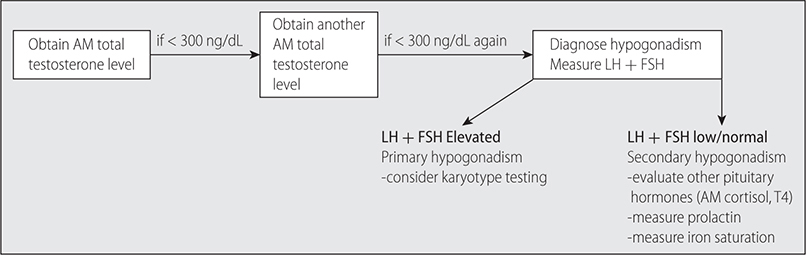
–See Fig. 21–2 for evaluation algorithm for suspected hypogonadism.
–Discuss risks, benefits, costs, and patient preferences in men with low testosterone and sexual dysfunction who desire to improve sexual function. (ACP)
–Measure serum estradiol in testosterone-deficient patients who present with breast symptoms or gynecomastia prior to the commencement of testosterone therapy. (EAU)
–Obtain a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan for all men with severe androgen deficiency.
FIG. 21–2 EVALUATION OF SUSPECTED MALE HYPOGONADISM.
Management
–Testosterone therapy is indicated for androgen deficiency syndromes (low testosterone with symptoms) unless contraindications exist.1
–Do not start treatment for goals of improving energy, vitality, physical function, or cognition. (ACP)
–Consider IM over transdermal therapy, given lower cost with similar risks and efficacy. (ACP)
–Obtain a hemoglobin and hematocrit (and PSA in men over 40 y) prior to initiating testosterone therapy and educate patients about the risk of polycythemia. (EAU)
–Adjust testosterone therapy dosing to achieve a total testosterone level in the middle tertile of the normal reference range. (AUA)
–Monitor clinical response to therapy, testosterone level, PSA, digital prostate exam, and hematocrit 3, 6, and 12 mo after starting therapy, and annually thereafter. (EAU)
–Consider stopping testosterone therapy after 3–6 mo in patients who normalized total testosterone levels but fail to achieve improvement in clinical signs or symptoms. (AUA)
Practice Pearl
• Testosterone therapy options (goal is a total testosterone level in mid-normal range):
- Testosterone enanthate or cypionate: 150–200 mg IM every 2 wk, or 75–100 mg IM weekly.
- Testosterone transdermal patch: 4–6 mg daily.
- Testosterone 1% gel: 50–100 mg daily.
- Testosterone 2% gel: 10–70 mg daily.
- Testosterone 2% solution: 60–120 mg (2–4 pumps or twists) applied to the axillae daily.
- Testosterone buccal bioadhesive tablets: 30 mg to buccal mucosa q 12 h.
- Testosterone nasal gel: 11 mg (2 pump actuations, 1 actuation per nostril) TID.
Sources
–https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/103/5/1715/4939465
–https://uroweb.org/guideline/male-hypogonadism/
–http://www.auanet.org/guidelines/testosterone-deficiency-(2018)#x7697