Population: Adults with AF.
Organizations
 AAFP 2017, AHA/ACC 2019, ESC 2015
AAFP 2017, AHA/ACC 2019, ESC 2015
Prevention Recommendations
–Discuss risk of stroke and bleeding with patients considering anticoagulation. Estimate stroke risk with CHA2DS2-VASc score (see Table 19–5). Estimate bleeding risk with HAS-BLED or ORBIT (see Tables 19–6 and 19–7).
TABLE 19–5 STROKE RISK STRATIFICATION WITH THE CHADS2 AND CHA2DS2-VASc SCORES
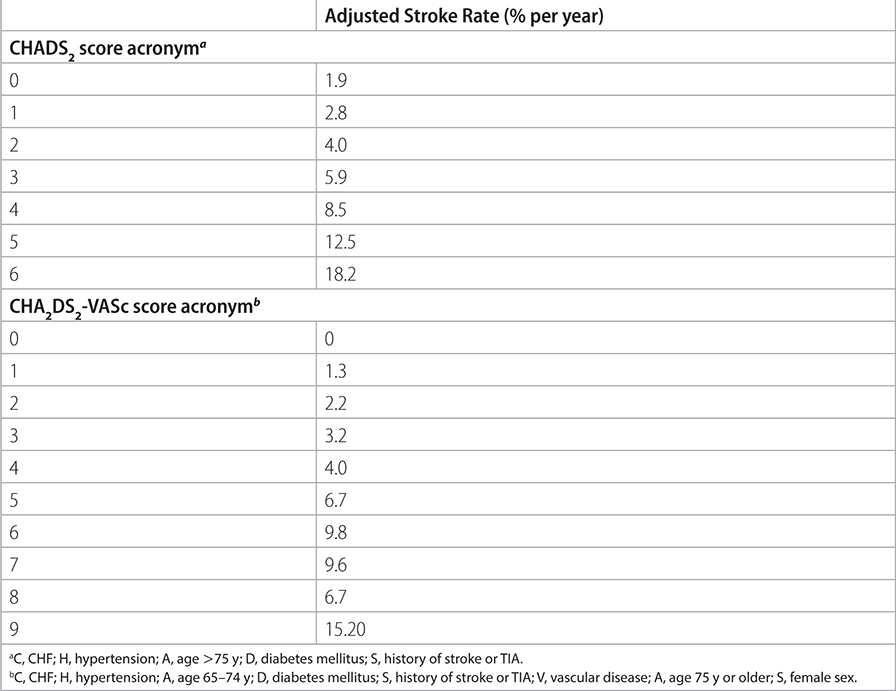
TABLE 19–6 HAS-BLED BLEEDING RISK SCORE FOR WARFARIN THERAPY
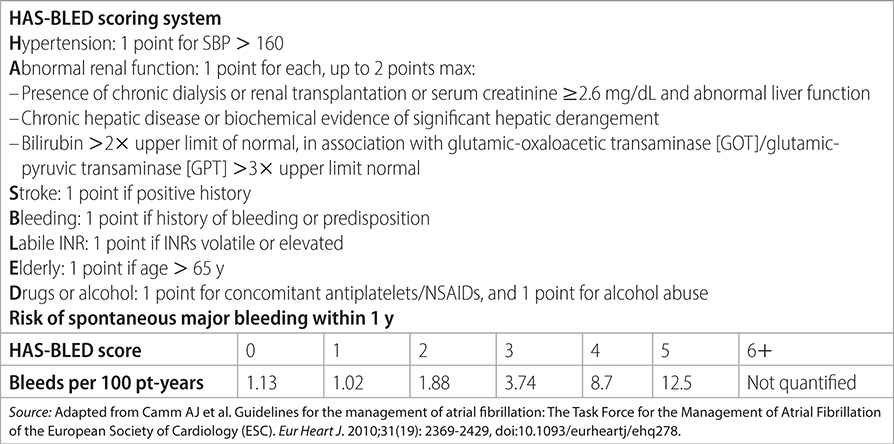
TABLE 19–7 THROMBOEMBOLIC RISK SCORES IN NONVALVULAR ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
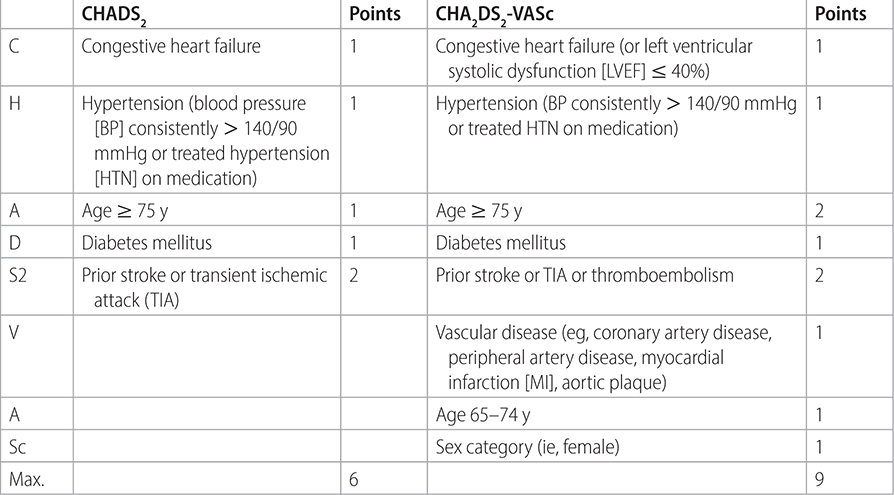
–Use CHA2DS2-VASc1 score to determine need for anticoagulation.
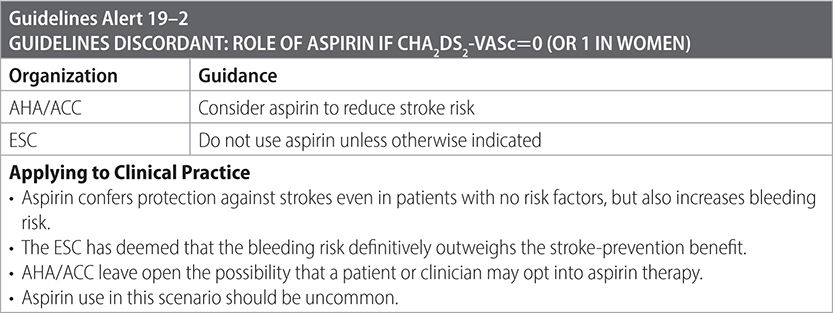
• CHA2DS2-VASc 0 in men or 1 in women: see Guidelines Alert 19–2.
• CHA2DS2-VASc 1 in men or 2 in women: consider anticoagulation after discussion of stroke and bleeding risks.
• CHA2DS2-VASc ≥2 in men or ≥3 in women: anticoagulate.
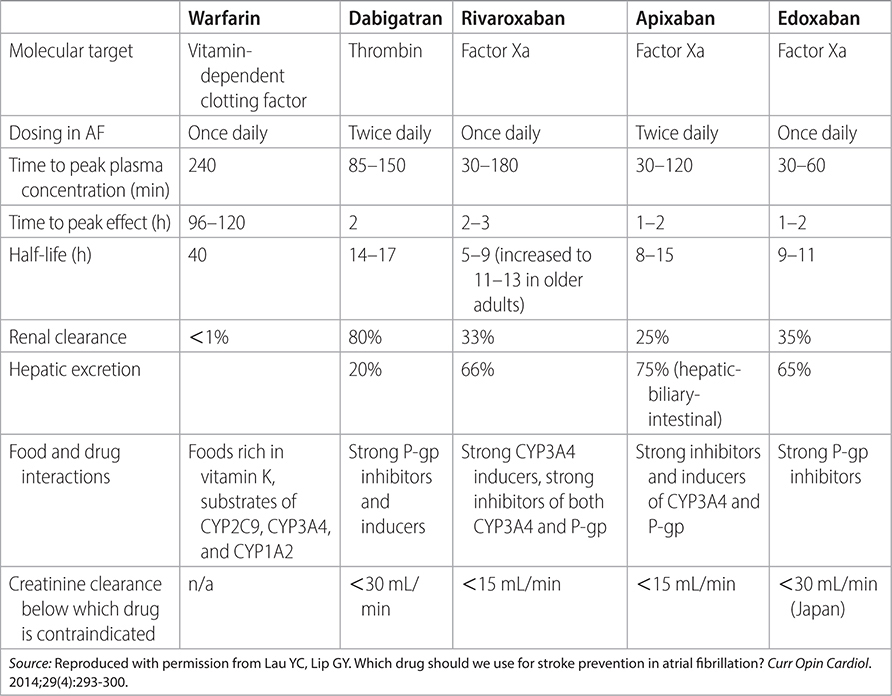
–Choose direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC; apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban, or rivaroxaban) over warfarin, except for select patients with valvular disease. See Table 19–8 for more information about choice of DOAC.
–Use warfarin, not a DOAC, in severe mitral stenosis, mechanical heart valves, or in the first 3 mo after bioprosthetic valve replacement. Titrate to international normalized ratio (INR) of 2–3 or 2.5–3.5, depending on the type and location of prosthesis.
TABLE 19–8 COMPARING WARFARIN WITH DOACS
–In patients treated with warfarin, obtain INR weekly until INR is stable and at least monthly when INR is in range and stable. (AHA/ACC)
–Do not give dual treatment with anticoagulant and antiplatelet therapy. Anticoagulant takes precedence.
–Following coronary revascularization (PCI or surgical) in patients with CHA2DS2-VASc ≥ 2, use clopidogrel without aspirin alongside OAC. (AHA/ACC)

Interrupting and Bridging Anticoagulation
–Bridge therapy with unfractionated heparin or LWMH only for patients with AF and mechanical heart valve undergoing procedures that require interruption of warfarin. Otherwise, bridging is not required.
–When switching from vitamin K antagonist (warfarin) to non-vitamin K antagonist, start the DOAC as soon as the INR is <2.0. If INR is 2.0–2.5, start DOAC the following day. If INR is ≥2.5, recheck INR in 1–3 d.
–When switching from non–vitamin K antagonist to warfarin, administer both concomitantly until the INR is in the therapeutic range.
Practice Pearls
• Average stroke rate in patients with risk factors is approximately 5% per year.
• Adjusted-dose warfarin and antiplatelet agents reduce absolute risk of stroke.
• Women have a higher prevalence of stroke than men.
• Women have unique risk factors for stroke, such as pregnancy, hormone therapy, and higher prevalence of hypertension in older ages.
• In patients age 80+, a lower dose of edoxaban (15 mg daily) reduces stroke risk. (N Engl J Med. 2020;383(18):1735–1745)
Sources
–Am Fam Physician. 2017;96(5):332-333.
–Circulation. 2014;130(23):e199-e267.
–JAMA. 2015;313(19):1950-1962.
– 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS Focused Update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS. Guideline for the Management of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation.
Population: Patients with AF and acute transient ischemic attack (TIA) or ischemic stroke.
Organization
 ESC 2016
ESC 2016
Recommendations
–When to start oral anticoagulation after stroke or TIA:
• TIA: 1 d after acute event.
• Mild stroke (NIHSS < 8): 3 d after acute event.
• Moderate stroke (NIHSS 8–15): evaluate hemorrhagic transformation by CT or MRI at day 6, then start DOAC 6 d after acute event.
• Severe stroke (NIHSS > 16): evaluate hemorrhagic transformation.
Source
–Eur Heart J. 2016;37:2893-2962.