Return to drug monograph
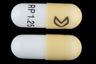
Drug Name: Ramipril 1.25 MG Oral Capsule
Pill Image:
Ingredient(s): Ramipril
Imprint: RP;1;25
Color(s): Yellow
Shape: Capsule
Size (mm): 14.00
Score: 1
Inactive Ingredient(s): starch, corn / gelatin / titanium dioxide / ferric oxide yellow
Drug Label Author:
Cobalt Laboratories Inc.
DEA Schedule:
Non-Scheduled
 [
[