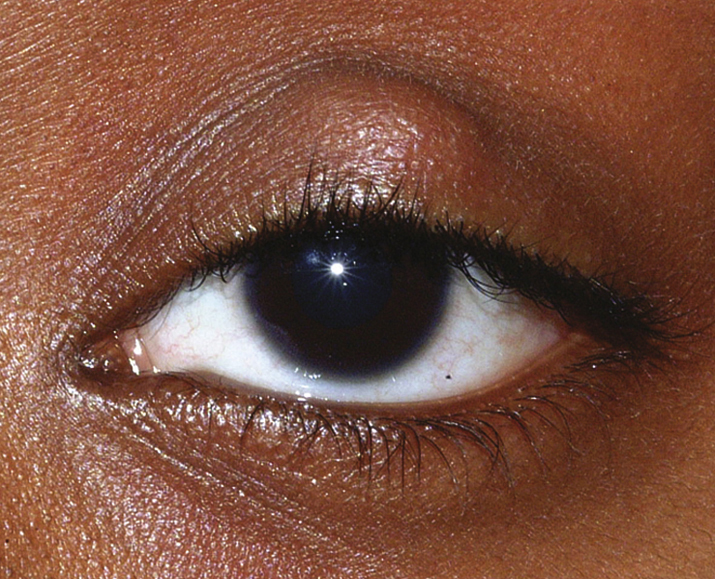
(See Figure 6.2.1.)
Critical
Visible or palpable, well-defined, subcutaneous nodule in the eyelid. In some cases, a nodule cannot be identified.
Other
Blocked meibomian gland orifice, eyelid swelling and erythema, focal tenderness, associated blepharitis, or acne rosacea. May also note lesion coming to a head or draining mucopurulent material.
Definitions
Chalazion: Focal, tender, or nontender inflammation within the eyelid secondary to obstruction of a meibomian gland or gland of Zeis.
Hordeolum: Acute, tender infection; can be external (abscess of a glands of Zeis on eyelid margin) or internal (abscess of the meibomian gland). Usually involves Staphylococcus species and occasionally evolves into preseptal cellulitis.