Visual loss; severity depends on the region of involvement. History of high-velocity missile injury to orbit (e.g., a BB, bullet, or shrapnel).
(See Figure 3.15.1.)
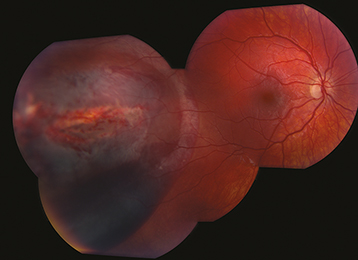
Full-thickness rupture of the choroid and retina leaving bare sclera visible on fundus examination, typically demonstrating a “claw-like” configuration of fundus atrophy and pigmentation. The globe remains intact.
Subretinal, intraretinal, preretinal, and VH often involving the macula. Eventually blood is resorbed and the resultant defects are replaced by fibrous tissue. Intraorbital foreign body. Can have associated avulsion of vitreous base, which can cause peripheral retinal dialysis.
Caused by a high-velocity missile passing through the orbit without perforating the globe. Resultant shock waves lead to chorioretinal rupture from the sclera.
Ruptured globe: Severe subconjunctival hemorrhage and chemosis, often with deep or shallow AC; low IOP; and peaked, irregular pupil. See 3.10, Ruptured Globe and Penetrating Ocular Injury.
Choroidal rupture: White or yellow crescent-shaped subretinal streak usually concentric to the optic nerve. No retinal break is present. Initially, retinal hemorrhage in the posterior pole may obscure a choroidal rupture, which subsequently becomes apparent as the blood clears. See 3.14, Traumatic Choroidal Rupture.
Optic nerve avulsion: Decreased vision with a RAPD on examination and hemorrhagic depression or excavation of the optic disc if partial, or retraction of entire nerve if complete. Often associated with VH. No treatment is available, and visual prognosis depends on extent of injury. See 3.21, Traumatic Optic Neuropathy.
Complete ocular evaluation including dilated fundus examination. Look for areas of retinal and choroidal rupture with underlying bare sclera. Carefully examine the conjunctiva and sclera to rule out ruptured globe. Rule out IOFB. Carefully examine the retinal periphery for retinal tears or dialysis.
CT scan of the orbit (axial, coronal, and parasagittal views, 1-mm sections) to check for intrascleral, intraocular, or intraorbital foreign bodies. Gentle B-scan US or UBM may be helpful to rule out intraocular or intraorbital foreign bodies.
Observation, as there is no effective treatment. Complications, including retinal dialysis and detachment, are treated appropriately. Surgery can be considered for nonclearing VH.
Sequential examinations are required every 2 to 4 weeks initially looking for signs of retinal detachment as blood clears. Patients should be followed until an atrophic “claw-like” scar replaces areas of hemorrhage.