DESCRIPTION 
- Noonan syndrome is a Mendelian inherited syndrome characterized by phenotypic stigmata differentiated from those seen with the genotype of Turner syndrome (XO).
- System(s) affected: Cardiovascular; endocrine; urologic; otologic; neurologic; hematologic
- Synonym(s): Female pseudo-Turner syndrome; Male Turner syndrome; Bonnevie Ullrich syndrome
EPIDEMIOLOGY 
- Age at presentation: Fetal to adult; the mean age at diagnosis is ~9 yr.
- Sex: Male = Female
Prevalence 
Overall prevalence is not well established, but is ~1/2,000 newborns, with males affected as often as females.
RISK FACTORS
Genetics 
- An autosomal-dominant and recessive patterns of inheritance has been established. Many cases may be new stigmata. Normal karyotype.
- Marked genetic heterogeneity
- To date, familial pedigree studies have isolated the locus of Noonan syndrome to several chromosomes, including 12 and 18.
- A large proportion (20–30%) of 1st-generation family members of individuals with Noonan syndrome also are affected with Noonan syndrome. Affected parents 30–75%.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY 
Depends on associated cardiac defects.
ETIOLOGY 
Hormonal: Mutations in PTPN11 gene on chromosome 12 resulting in interference with growth hormone and IGF-I signaling in 50% of patients.
COMMONLY ASSOCIATED CONDITIONS 
- Cardiovascular (50% of cases):
- Pulmonary valve dysplasia and stenosis is the most common lesion (50–75% of cases).
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Typically asymmetric; can be associated with subaortic or subpulmonic stenosis (25–33% of affected individuals)
- Atrial septal defect (ASD): 27% of cases
- Tetralogy of Fallot
- Conduction abnormalities
- Rarely aortic stenosis and coarctation
- Endocrine/urologic:
- Gonadal dysfunction: Hypofunction of testes in males
- Cryptorchidism
- Short stature
- Renal/Genitourinary abnormalities
- Otologic/Ophthalmologic:
- Progressive sensorineural hearing deficits (50% of cases)
- Strabismus, refractive errors, amblyopia, and nystagmus (95%)
- Neuropsychological:
- Mental retardation (25% of cases)
- Developmental delay
- Hematologic/Oncologic:
- Coagulopathies
- Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia or "benign" monoclonal gammopathy
- Malignant schwannoma
- Neurologic:
- Cerebrovascular disease such as moyamoya
- Lymphatic:
- Postnatal: Dorsal limb lymphedema, organ lymphangiectasias, chylous effusions
- Prenatal: Cystic hygroma, polyhydramnios, hydrops fetalis
Outline
Signs and symptoms:
The phenotype varies with the age at presentation
- Fetal:
- Increased nuchal fluid
- Possible hydrops
- Pleural effusions
- Normal karyotype on amniocentesis
- Brachycephaly or growth retardation
- Shortened femora
- Renal abnormalities
- Infant:
- Cardiac abnormalities:
- Systolic ejection murmur of pulmonary stenosis
- Ejection click usually not present
- If LV cardiomyopathy is present, the patient may have typical symptoms of exertional dyspnea, chest pain, palpitations, postural hypotension, or syncope.
- Edema of hands and feet
- High-arched palate
- Short or webbed neck
- Pectus carinatum or excavatum
- Cubitus valgus
- Typical facies: Malformed posteriorly rotated ears, antimongoloid palpebral slant, ptosis, broad flat nose, vivid blue or blue-green irises, thick/droopy eyelids
- Undescended testes with possible hypogonadism
- Cardiovascular malformations: Predominantly ASD, pulmonary stenosis, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy may result in symptoms if severe.
- Childhood and adolescence:
- Short stature
- Developmental delay
- Characteristic cardiac malformations
- Sexual maturation delay of ~2 yr
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS & INTERPRETATION 
- Echo:
- Isolated pulmonary stenosis or peripheral pulmonary artery stenosis may result in RV hypertrophy.
- If associated with asymmetric LV hypertrophy, left-axis deviation with LV hypertrophy may be seen.
- Conduction abnormalities: Typically 1st-degree atrioventricular block
- Audiometry:
- Sensorineural or conductive hearing losses
- Developmental/psychosocial testing:
- May reveal varying degrees of cognitive, behavioral, and psychosocial deficits
Imaging 
- Fetal US:
- Subcutaneous edema of nuchal skin folds
- Generalized fetal edema
- Renal abnormalities
- Short femora
- Cardiac abnormalities
- Transthoracic or fetal echo:
- Pulmonary stenosis, ASD, asymmetric hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, tetralogy of Fallot, rarely aortic stenosis
- Radiographs:
- Chest: Enlarged cardiac silhouette secondary to LV or RV hypertrophy
- Extremity: Bone age studies in association with growth hormone therapy for growth retardation
Lab 
Genetic testing:
- PTPN11 gene on Chr 12q24.1 (50%), KRAS gene mutations (<5%), SOS1 (13%), RAF1 (3–17%)
- Sources: Blood, chorionic villi and amniotic fluid, coagulation profiles, platelet count, VWF levels, coagulation factor levels
Diagnostic Procedures/Surgery 
Cardiac catheterization:
- Diagnostic catheterization rarely required
- Pulmonary stenosis with doming or dysplastic pulmonary valve
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with possible ventricular outflow tract obstruction
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS 
- Turner syndrome
- Cardio-facial-cutaneous syndrome
- LEOPARD syndrome
- Costello syndrome
- Watson syndrome
- Neurofibromatosis: In the context of isolated pulmonary stenosis or peripheral artery stenosis, may display right-axis deviation and RV hypertrophy
Outline
FOLLOW-UP RECOMMENDATIONS
Patient Monitoring 
- Routine lifelong outpatient visits are recommended, with attention to systems discussed, especially cardiovascular, renal, endocrine, and otologic.
- A well-coordinated multidisciplinary approach is required.
DIET 
No dietary restrictions
PATIENT EDUCATION 
Activity: No restrictions in the absence of cardiac disease
PROGNOSIS 
Overall, the prognosis and outcomes have improved significantly due to early recognition and treatment of associated cardiac malformations, short stature, and cognitive delays.
Pregnancy Considerations 
Pregnancy is possible, but may be of high risk in women with severe manifestations; 50% of offspring of affected mothers or fathers will have Noonan syndrome.
Outline

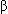 -Adrenergic receptor–blocking agents such as
-Adrenergic receptor–blocking agents such as