A.2. How are TAAs and thoracoabdominal aneurysms (TAAAs) classified?
Answer:
TAAs do not follow a specific classification system but are described by the extent of the aorta that is involved, including the aortic root, ascending aorta, aortic arch, and descending thoracic aorta. TAAAs are described using the modified Crawford classification, which subdivides TAAAs into five types according to the extent of the surgical repair required (Figure 9.4).
Figure 9.4.: The Modified Crawford Classification of Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysms.
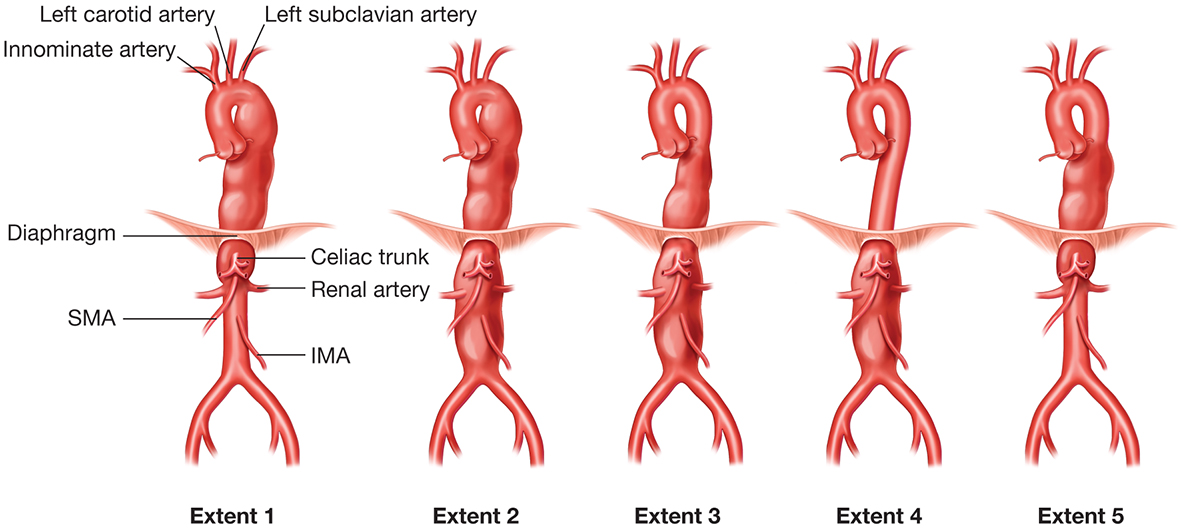
The modified Crawford classification of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms. (Reprinted with permission from Bolman R, Kaneko T. Open thoracoabdominal aneurysm repair. In: Darling RC, Ozaki CK, eds. Vascular Surgery: Arterial Procedures. Wolters Kluwer; 2016:74.)
Type I begins distal to the left subclavian artery (LSCA) and extends down below the diaphragm to above the renal arteries.
Type II begins distal to the left subclavian above the sixth intercostal space. It extends through the diaphragm and ends below the renal arteries.
Type III begins below the sixth intercostal space but above the diaphragm. It extends below the renal arteries.
Type IV begins below the diaphragm but above the renal arteries, with extension to below the renal arteries.
Type V begins above the diaphragm and ends above the renal arteries.
References
- Crawford ES, Crawford JL, Safi HJ, et al. Thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms: preoperative and intraoperative factors determining immediate and long-term results of operations in 605 patients. J Vasc Surg. 1986;3:389-404.
- Frederick JR, Woo YJ. Thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm. Ann Cardiothorac Surg. 2012;1:277-285.
- Hoel AW. Aneurysmal disease: thoracic aorta. Surg Clin North Am. 2013;93:893-910.


