In many circumstances, more than a single acid-base disturbance exists. Examples include combined metabolic and respiratory acidosis with cardiogenic shock; metabolic alkalosis and anion-gap acidosis in pts with vomiting and diabetic ketoacidosis; and anion-gap metabolic acidosis with respiratory alkalosis in pts with salicylate toxicity. The diagnosis may be clinically evident and/or suggested by relationships between the PCO2 and [HCO3-] that diverge from those found in simple disorders. For example, the PCO2 in a pt with metabolic acidosis and respiratory alkalosis will be considerably less than that predicted from the [HCO3-] and Winter's formula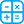 [PaCO2 = (1.5 × [HCO3-]) + 8 + 2].
[PaCO2 = (1.5 × [HCO3-]) + 8 + 2].
In “simple” anion-gap acidosis, the anion gap increases in proportion to the fall in [HCO3-]. A lesser drop in serum [HCO3-] than in the anion gap suggests a coexisting metabolic alkalosis. Conversely, a proportionately larger drop in [HCO3-] than in the anion gap suggests the presence of a mixed anion-gap and non-anion-gap metabolic acidosis. Notably, however, these interpretations assume 1:1 relationships between unmeasured anions and the fall in [HCO3-], which are not uniformly present in individual pts or as acidoses evolve. For example, volume resuscitation of pts with DKA will typically increase glomerular filtration and the urinary excretion of ketones, resulting in a decrease in the anion gap in the absence of a supervening non-anion-gap acidosis.
For a more detailed discussion, see Mount DB: Fluid and Electrolyte Disturbances, Chap. 63, p. 295; and DuBose TD Jr: Acidosis and Alkalosis, Chap. 66, p. 315, in HPIM-19. See also Mount DB, Zandi-Nejad K: Disorders of potassium balance, in The Kidney, 9th ed, BM Brenner (ed). Philadelphia, Saunders, 2011; and Ellison DH, Berl T: Clinical practice. The syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis. N Engl J Med 356:2064, 2007; Perianayagam A et al: DDAVP is effective in preventing and reversing inadvertent overcorrection of hyponatremia. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3:331, 2008; Sood L et al: Hypertonic saline and desmopressin: a simple strategy for safe correction of severe hyponatremia. Am J Kidney Dis 61:571-578, 2013. |